Question 271
You recently developed an application that monitors a large number of stock prices. You need to configure Pub/Sub to receive messages and update the current stock price in an in-memory database. A downstream service needs the most up-to-date prices in the in-memory database to perform stock trading transactions. Each message contains three pieces or information:
• Stock symbol
• Stock price
• Timestamp for the update
How should you set up your Pub/Sub subscription?
A. Create a push subscription with exactly-once delivery enabled.
B. Create a pull subscription with both ordering and exactly-once delivery turned off.
C. Create a pull subscription with ordering enabled, using the stock symbol as the ordering key.
D. Create a push subscription with both ordering and exactly-once delivery turned off.
Question 272
You are a developer at a social media company. The company runs their social media website on-premises and uses MySQL as a backend to store user profiles and user posts. Your company plans to migrate to Google Cloud, and your learn will migrate user profile information to Firestore. You are tasked with designing the Firestore collections. What should you do?
A. Create one root collection for user profiles, and create one root collection for user posts.
B. Create one root collection for user profiles, and create one subcollection for each user's posts.
C. Create one root collection for user profiles, and store each user's post as a nested list in the user profile document.
D. Create one root collection for user posts, and create one subcollection for each user's profile.
Question 273
Your team recently deployed an application on Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE). You are monitoring your application and want to be alerted when the average memory consumption of your containers is under 20% or above 80%. How should you configure the alerts?
A. Create a Cloud Function that consumes the Monitoring API. Create a schedule to trigger the Cloud Function hourly and alert you if the average memory consumption is outside the defined range.
B. In Cloud Monitoring, create an alerting policy to notify you if the average memory consumption is outside the defined range.
C. Create a Cloud Function that runs on a schedule, executes kubectl top on all the workloads on the cluster, and sends an email alert if the average memory consumption is outside the defined range.
D. Write a script that pulls the memory consumption of the instance at the OS level and sends an email alert if the average memory consumption is outside the defined range.
Question 274
You manage a microservice-based ecommerce platform on Google Cloud that sends confirmation emails to a third-party email service provider using a Cloud Function. Your company just launched a marketing campaign, and some customers are reporting that they have not received order confirmation emails. You discover that the services triggering the Cloud Function are receiving HTTP 500 errors. You need to change the way emails are handled to minimize email loss. What should you do?
A. Increase the Cloud Function's timeout to nine minutes.
B. Configure the sender application to publish the outgoing emails in a message to a Pub/Sub topic. Update the Cloud Function configuration to consume the Pub/Sub queue.
C. Configure the sender application to write emails to Memorystore and then trigger the Cloud Function. When the function is triggered, it reads the email details from Memorystore and sends them to the email service.
D. Configure the sender application to retry the execution of the Cloud Function every one second if a request fails.
Question 275
You have a web application that publishes messages to Pub/Sub. You plan to build new versions of the application locally and need to quickly test Pub/Sub integration for each new build. How should you configure local testing?
A. In the Google Cloud console, navigate to the API Library, and enable the Pub/Sub API. When developing locally configure your application to call pubsub.googleapis.com.
B. Install the Pub/Sub emulator using gcloud, and start the emulator with a valid Google Project ID. When developing locally, configure your applicat.cn to use the local emulator by exporting the PUBSUB_EMULATOR_HOST variable.
C. Run the gcloud config set api_endpoint_overrides/pubsub https://pubsubemulator.googleapis.com.com/ command to change the Pub/Sub endpoint prior to starting the application.
D. Install Cloud Code on the integrated development environment (IDE). Navigate to Cloud APIs, and enable Pub/Sub against a valid Google Project IWhen developing locally, configure your application to call pubsub.googleapis.com.
Question 276
You recently developed an application that monitors a large number of stock prices. You need to configure Pub/Sub to receive a high volume messages and update the current stock price in a single large in-memory database. A downstream service needs the most up-to-date prices in the in-memory database to perform stock trading transactions. Each message contains three pieces or information:
• Stock symbol
• Stock price
• Timestamp for the update
How should you set up your Pub/Sub subscription?
A. Create a pull subscription with exactly-once delivery enabled.
B. Create a push subscription with both ordering and exactly-once delivery turned off.
C. Create a push subscription with exactly-once delivery enabled.
D. Create a pull subscription with both ordering and exactly-once delivery turned off.
Question 277
Your team has created an application that is hosted on a Google Kubemetes Engine (GKE) cluster. You need to connect the application to a legacy REST service that is deployed in two GKE clusters in two different regions. You want to connect your application to the legacy service in a way that is resilient and requires the fewest number of steps. You also want to be able to run probe-based health checks on the legacy service on a separate port. How should you set up the connection? (Choose two.)
A. Use Traffic Director with a sidecar proxy to connect the application to the service.
B. Set up a proxyless Traffic Director configuration for the application.
C. Configure the legacy service's firewall to allow health checks originating from the sidecar proxy.
D. Configure the legacy service's firewall to allow health checks originating from the application.
E. Configure the legacy service's firewall to allow health checks originating from the Traffic Director control plane.
Question 278
You are monitoring a web application that is written in Go and deployed in Google Kubernetes Engine. You notice an increase in CPU and memory utilization. You need to determine which function is consuming the most CPU and memory resources. What should you do?
A. Add print commands to the application source code to log when each function is called, and redeploy the application.
B. Create a Cloud Logging query that gathers the web application s logs. Write a Python script that calculates the difference between the timestamps from the beginning and the end of the application's longest functions to identify time-intensive functions.
C. Import OpenTelemetry and Trace export packages into your application, and create the trace provider. Review the latency data for your application on the Trace overview page, and identify which functions cause the most latency.
D. Import the Cloud Profiler package into your application, and initialize the Profiler agent. Review the generated flame graph in the Google Cloud console to identify time-intensive functions.
Question 279
You are developing a flower ordering application. Currently you have three microservices:
• Order Service (receives the orders)
• Order Fulfillment Service (processes the orders)
• Notification Service (notifies the customer when the order is filled)
You need to determine how the services will communicate with each other. You want incoming orders to be processed quickly and you need to collect order information for fulfillment. You also want to make sure orders are not lost between your services and are able to communicate asynchronously. How should the requests be processed?
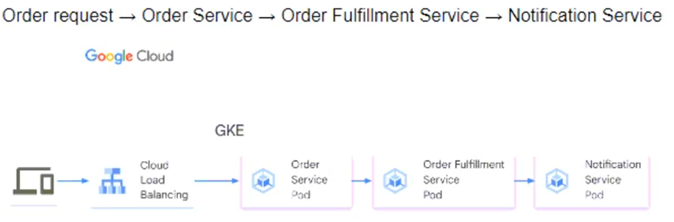
A.
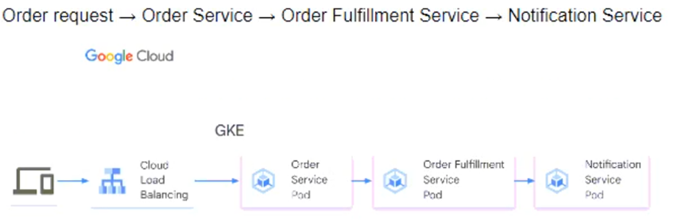
B.
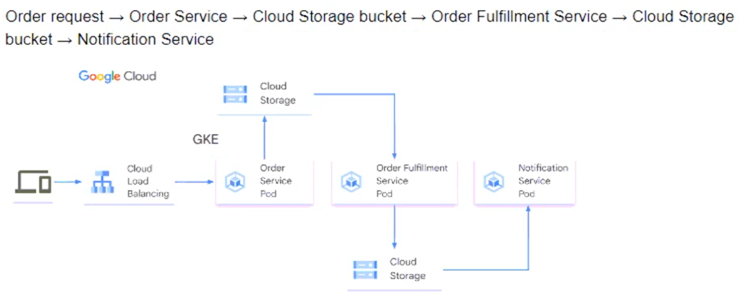
C.

D.
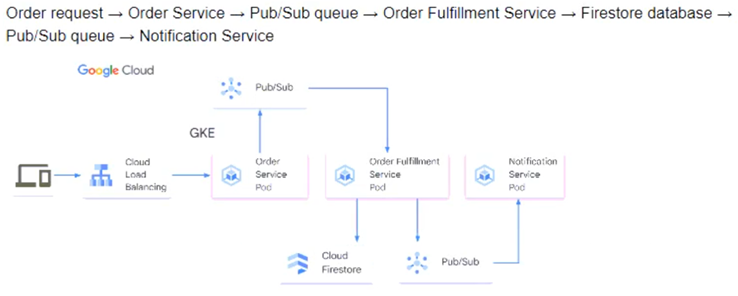
Question 280
You recently deployed an application to GKE where Pods are writing files to a Compute Engine persistent disk. You have created a PersistentVolumeClaim (PVC) and a PersistentVolume (PV) object on Kubernetes for the disk, and you reference the PVC in the deployment manifest file.
You recently expanded the size of the persistent disk because the application has used up almost all of the disk space. You have logged on to one of the Pods, and you notice that the disk expansion is not visible in the container file system. What should you do?
A. Set the spec.capacity.storage value of the PV object to match the size of the persistent disk. Apply the updated configuration by using kubectl.
B. Recreate the application Pods by running the kubectl delete deployment DEPLOYMENT_NAME && kubectl apply deployment.yaml command, where the DEPLOYMENT_NAME parameter is the name of your deployment and deployment.yaml is its manifest file.
C. Set the spec.resources.requests.storage value of the PVC object to match the size of the persistent disk. Apply the updated configuration by using kubectl.
D. In the Pod, resize the disk partition to the maximum value by using the fdisk or parted utility.




