Configuring Default Static Routes on Cisco Routers
Objective
The objective of this lab exercise is to learn and understand how to configure default static routes on Cisco IOS routers. By default, no default routes exist on Cisco IOS routers.
Purpose
Static default route configuration is a fundamental skill for network engineers. Default routes are used to forward traffic to destinations not in the router's routing table. They can also forward all external traffic, such as Internet traffic, to an Internet Service Provider. As a Cisco engineer or CCNA candidate, you must know how to configure static default routes.
Lab Topology
Use the following topology to complete this lab exercise:
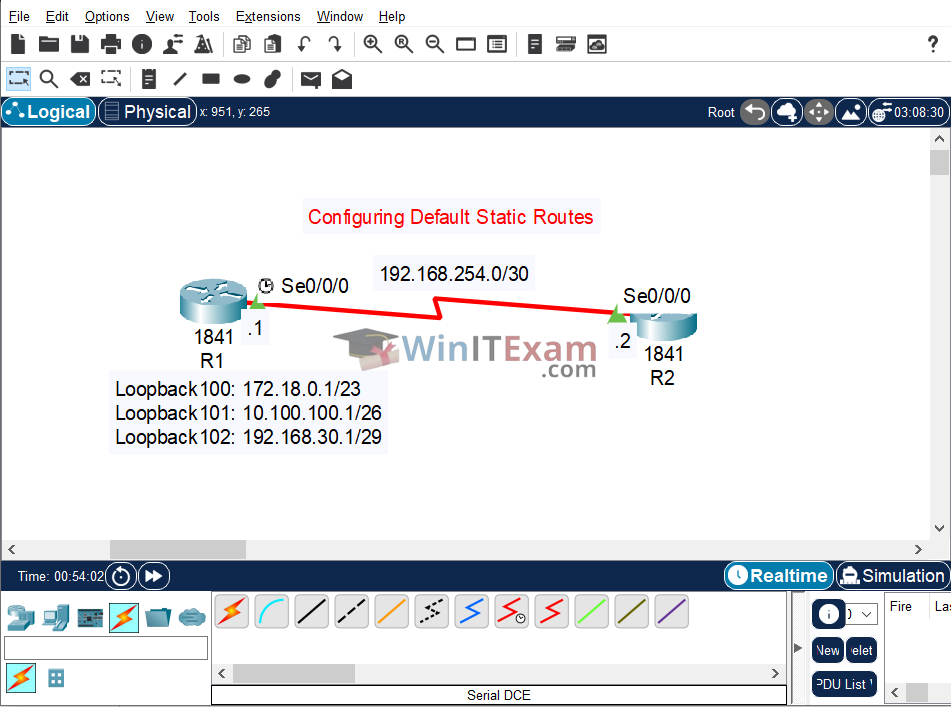
Task 1: Configure Hostnames
Objective: Set hostnames on R1 and R2 as illustrated in the topology.
Configuration:
R1#configure terminal R1(config)#hostname R1 R1(config)#end R2#configure terminal R2(config)#hostname R2 R2(config)#end
Task 2: Configure Serial Connection
Objective: Configure a back-to-back Serial connection between R1 and R2. Set the DCE interface Serial0/0/0 in R1 to provide clocking to R2 at a clock speed of 250 Kbps.
Configuration:
R1#configure terminal R1(config)#interface Serial0/0/0 R1(config-if)#clock rate 250000 R1(config-if)#exit
Task 3: Configure IP Addresses
Objective: Configure IP addresses 192.168.254.1/30 on R1 and 192.168.254.2/30 on R2's Serial0/0/0 interfaces. Also, configure the Loopback interfaces on R1 as illustrated in the topology.
Configuration:
R1#configure terminal R1(config)#interface Serial0/0/0 R1(config-if)#ip address 192.168.254.1 255.255.255.252 R1(config-if)#no shutdown R1(config-if)#exit R1(config)#interface Loopback100 R1(config-if)#ip address 172.18.0.1 255.255.254.0 R1(config-if)#exit R1(config)#interface Loopback101 R1(config-if)#ip address 10.100.100.1 255.255.255.192 R1(config-if)#exit R1(config)#interface Loopback102 R1(config-if)#ip address 192.168.30.1 255.255.255.248 R1(config-if)#exit R1#end R2#configure terminal R2(config)#interface Serial0/0/0 R2(config-if)#ip address 192.168.254.2 255.255.255.252 R2(config-if)#no shutdown R2(config-if)#end
Task 4: Configure Default Static Route
Objective: On R2, configure a static default route pointing to R1. Ping each Loopback interface configured on R1 from R2 to verify your static route configuration.
Configuration and Verification
R2#configure terminal
R2(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 Serial0/0/0
R2(config)#end
R2#show ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, I - IGRP, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP
i - IS-IS, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2, ia - IS-IS inter area
* - candidate default, U - per-user static route, o - ODR
P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is 0.0.0.0 to network 0.0.0.0
192.168.254.0/30 is subnetted, 1 subnets
C 192.168.254.0 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0
S* 0.0.0.0/0 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0
Note: The default route should appear as a candidate default route in the routing table.
R2#ping 172.18.0.1 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 172.18.0.1, timeout is 2 seconds: !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 11/13/15 ms R2#ping 10.100.100.1 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 10.100.100.1, timeout is 2 seconds: !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 10/14/23 ms R2#ping 192.168.30.1 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.30.1, timeout is 2 seconds: !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 12/15/23 ms
Cisco Packet Tracer file:
Load and open the .pkt Lab file in Cisco Packet Tracer from here: Configuring_Default_Static_Routes.pkt