Configuring IP Floating Static Routes on Cisco Routers
Objective
The objective of this lab exercise is to learn how to implement IP floating static route functionality on a Cisco router.
Purpose
Configuring a floating static route allows your Cisco router to have a backup route to a destination in case the primary route fails. This knowledge is essential for Cisco engineers and is part of the Cisco CCNA exam.
Lab Topology
Use the following topology to complete this lab exercise:
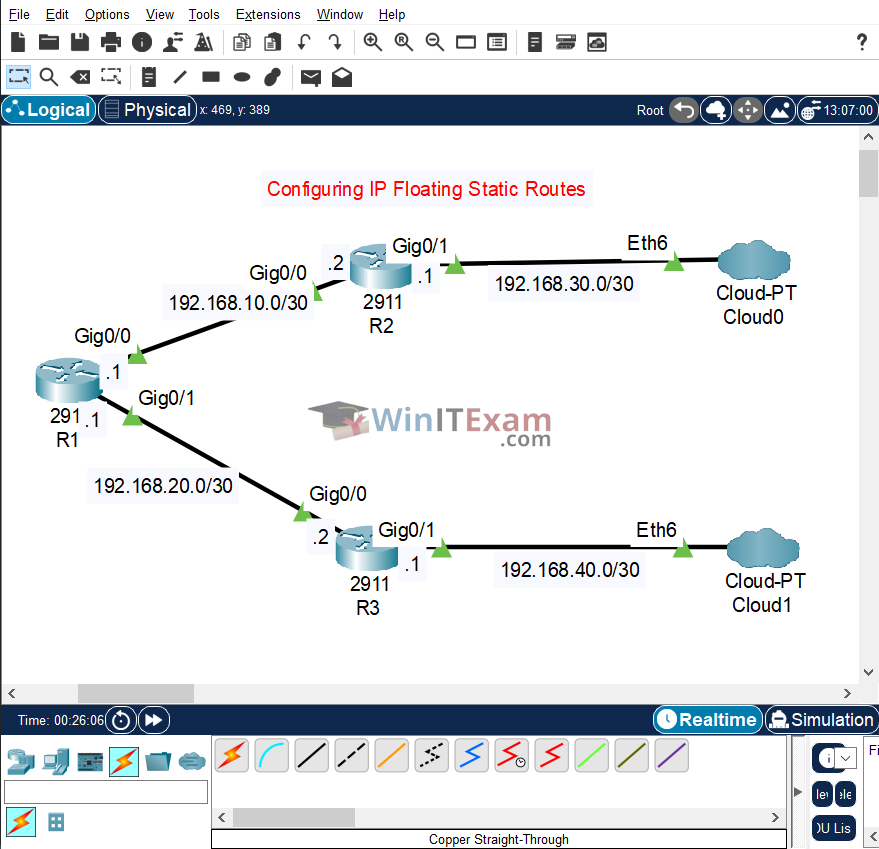
Note: Both R2 and R3 connect to the Internet, so R1 has two exit options to the Internet.
Task 1: Configure Hostnames
Objective: Set hostnames on R1, R2, and R3 as illustrated in the topology.
Configuration:
R1#configure terminal R1(config)#hostname R1 R1(config)#end R2#configure terminal R2(config)#hostname R2 R2(config)#end R3#configure terminal R3(config)#hostname R3 R3(config)#end
Task 2: Configure IP Addresses
Objective: Configure the IP addresses on the Gig0/0 and Gig0/1 interfaces of R1, R2, and R3 as illustrated in the topology.
Note: R1 will always have the .1 IP in each of its Gig interfaces. R2 and R3 will have the .1 IP on the Gig0/1 interface.
Configuration:
R1#configure terminal R1(config)#interface gigabitEthernet0/0 R1(config-if)#no shutdown R1(config-if)#ip address 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.252 R1(config-if)#exit R1(config)#interface gigabitEthernet0/1 R1(config-if)#no shutdown R1(config-if)#ip address 192.168.20.1 255.255.255.252 R1(config-if)#end R2#configure terminal R2(config)#interface gigabitEthernet0/0 R2(config-if)#no shutdown R2(config-if)#ip address 192.168.10.2 255.255.255.252 R2(config-if)#exit R2(config)#interface gigabitEthernet0/1 R2(config-if)#no shutdown R2(config-if)#ip address 192.168.30.1 255.255.255.252 R2(config-if)#end R3#configure terminal R3(config)#interface gigabitEthernet0/0 R3(config-if)#no shutdown R3(config-if)#ip address 192.168.20.2 255.255.255.252 R3(config-if)#exit R3(config)#interface gigabitEthernet0/1 R3(config-if)#no shutdown R3(config-if)#ip address 192.168.40.1 255.255.255.252 R3(config-if)#end
Task 3: Configure Default Static Routes
Objective: Configure two default static routes on R1. The first one (primary) will go to R2 with an administrative distance of 1. The secondary one will go to R3 with an administrative distance of 254. This ensures all traffic to unknown destinations is sent via R2.
Configuration:
R1#configure terminal R1(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.10.2 R1(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.20.2 254 R1(config)#end
Task 4: Test Floating Static Route
Objective: Shut down the interface Gig0/0 of R1 and use show commands to observe how the secondary route activates.
R1#sh ip route
Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP
i - IS-IS, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2, ia - IS-IS inter area
* - candidate default, U - per-user static route, o - ODR
P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is 192.168.10.2 to network 0.0.0.0
192.168.10.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.10.0/30 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0
L 192.168.10.1/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0
192.168.20.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.20.0/30 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1
L 192.168.20.1/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1
S* 0.0.0.0/0 [1/0] via 192.168.10.2
R1#conf t
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
R1(config)#interface gigabitEthernet0/0
R1(config-if)#shutdown
R1(config-if)#end
R1#show ip route
Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP
i - IS-IS, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2, ia - IS-IS inter area
* - candidate default, U - per-user static route, o - ODR
P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is 192.168.20.2 to network 0.0.0.0
192.168.20.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.20.0/30 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1
L 192.168.20.1/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1
S* 0.0.0.0/0 [254/0] via 192.168.20.2
R1#show ip interface brief
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
GigabitEthernet0/0 192.168.10.1 YES manual administratively down down
GigabitEthernet0/1 192.168.20.1 YES manual up up
GigabitEthernet0/2 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
Vlan1 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
Task 5: Restore Primary Route
Objective: Bring the interface Gig0/0 of R1 up again and verify how it re-establishes the primary route due to the lower administrative distance.
Configuration:
R1#configure terminal
R1(config)#interface gigabitEthernet0/0
R1(config-if)#no shutdown
R1(config-if)#end
R1#show ip route
Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP
i - IS-IS, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2, ia - IS-IS inter area
* - candidate default, U - per-user static route, o - ODR
P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is 192.168.10.2 to network 0.0.0.0
192.168.10.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.10.0/30 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0
L 192.168.10.1/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0
192.168.20.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.20.0/30 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1
L 192.168.20.1/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1
S* 0.0.0.0/0 [1/0] via 192.168.10.2
R1#show ip interface brief
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
GigabitEthernet0/0 192.168.10.1 YES manual up up
GigabitEthernet0/1 192.168.20.1 YES manual up up
GigabitEthernet0/2 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
Vlan1 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
Cisco Packet Tracer file:
Load and open the .pkt Lab file in Cisco Packet Tracer from here: Configuring_IP_Floating_Static_Routes.pkt