Understanding ARP and Proxy ARP on Cisco Routers
Objective
Learn and understand how ARP and Proxy ARP are used by routers to encapsulate packets before sending them to a neighboring device.
Purpose
Understanding ARP is crucial for passing the CCNA exam. You may encounter ARP-related issues to troubleshoot both in the exam and in real-world scenarios.
Lab Topology
Use the following topology to complete this lab exercise:
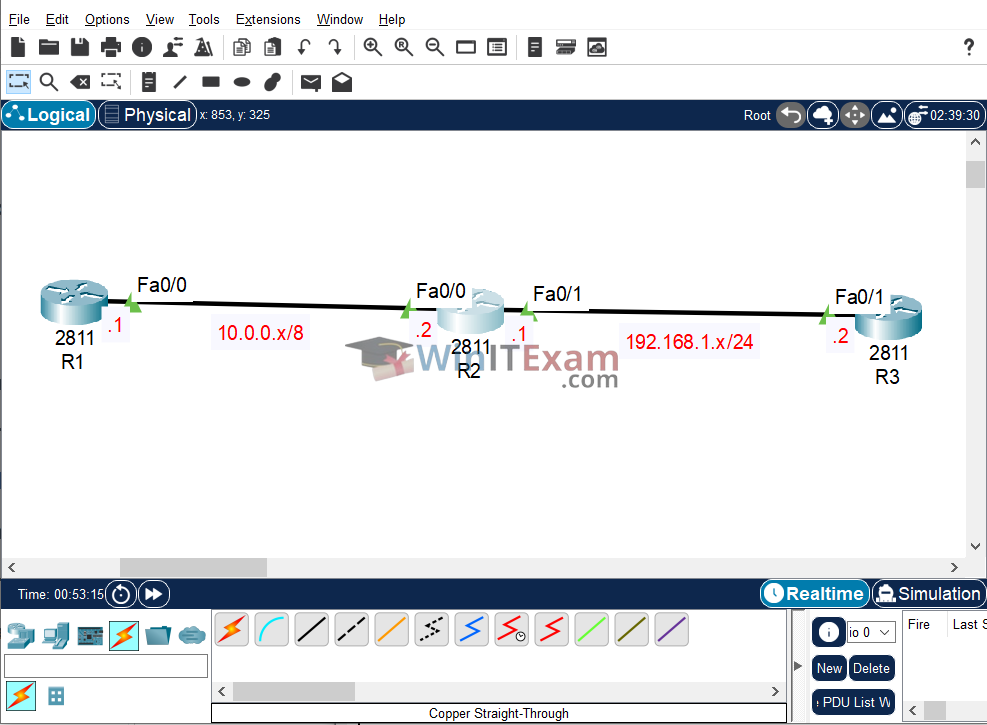
Task 1: Configure Hostnames
Objective: Set hostnames on routers R1, R2, and R3 as per the topology.
Configuration Steps:
Router#config t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CTRL/Z. Router(config)#hostname R1 R1(config)# Router#config t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CTRL/Z. Router(config)#hostname R2 R2(config)# Router#config t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CTRL/Z. Router(config)#hostname R3 R3(config)#
Task 2: Configure IP Addresses and Static Routes
Objective: Configure the IP addresses on the Ethernet interfaces of R1, R2, and R3 as illustrated in the topology (.1 for R1 and .2 for R2, and then .1 and .2 between R2 and R3). Add static routes so that R1 can ping the host address on R3 and R3 can return the ping.
Configuration Steps:
R1(config)#int f0/0 R1(config-if)#ip address 10.0.0.1 255.0.0.0 R1(config-if)#no shutdown R1(config-if)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 f0/0 R1(config)#end R1#copy running-config startup-config R2(config)#int f0/0 R2(config-if)#ip address 10.0.0.2 255.0.0.0 R2(config-if)#no shutdown R2(config)#int f0/1 R2(config-if)#ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 R2(config-if)#no shutdown R1(config)#end R1#copy running-config startup-config R3(config)#int f0/1 R3(config-if)#ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 R3(config-if)#no shutdown R3(config-if)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 f0/1 R1(config)#end R1#copy running-config startup-config
Task 3: Verify ARP Configuration
Objective: Use the correct show commands to check:
Verification Commands:
R1#show arp Protocol Address Age (min) Hardware Addr Type Interface Internet 10.0.0.1 - 00D0.5898.7B01 ARPA FastEthernet0/0 R1#ping 10.0.0.2 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 10.0.0.2, timeout is 2 seconds: .!!!! Success rate is 80 percent (4/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 0/0/0 ms R1#show arp Protocol Address Age (min) Hardware Addr Type Interface Internet 10.0.0.1 - 00D0.5898.7B01 ARPA FastEthernet0/0 Internet 10.0.0.2 0 0001.4313.3501 ARPA FastEthernet0/0 R1#ping 192.168.1.2 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.1.2, timeout is 2 seconds: ...!! Success rate is 40 percent (2/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 0/0/1 ms R1#show arp Protocol Address Age (min) Hardware Addr Type Interface Internet 10.0.0.1 - 00D0.5898.7B01 ARPA FastEthernet0/0 Internet 10.0.0.2 11 0001.4313.3501 ARPA FastEthernet0/0 Internet 192.168.1.2 0 0001.4313.3501 ARPA FastEthernet0/0 R3#show int f0/1 FastEthernet0/1 is up, line protocol is up (connected) Hardware is Lance, address is 0002.1769.e102 (bia 0002.1769.e102) Internet address is 192.168.1.2/24 R1#show arp Protocol Address Age (min) Hardware Addr Type Interface Internet 10.0.0.1 - 00D0.5898.7B01 ARPA FastEthernet0/0 Internet 10.0.0.2 13 0001.4313.3501 ARPA FastEthernet0/0 Internet 192.168.1.2 1 0001.4313.3501 ARPA FastEthernet0/0
Cisco Packet Tracer file:
Load and open the .pkt Lab file in Cisco Packet Tracer from here: ARP_and_Proxy_ARP.pkt