Question 261
You have a web application that publishes messages to Pub/Sub. You plan to build new versions of the application locally and want to quickly test Pub/Sub integration for each new build. How should you configure local testing?
A. Install Cloud Code on the integrated development environment (IDE). Navigate to Cloud APIs, and enable Pub/Sub against a valid Google Project ID. When developing locally, configure your application to call pubsub.googleapis.com.
B. Install the Pub/Sub emulator using gcloud, and start the emulator with a valid Google Project ID. When developing locally, configure your application to use the local emulator with ${gcloud beta emulators pubsub env-init}.
C. In the Google Cloud console, navigate to the API Library, and enable the Pub/Sub API. When developing locally, configure your application to call pubsub.googleapis.com.
D. Install the Pub/Sub emulator using gcloud, and start the emulator with a valid Google Project IWhen developing locally, configure your application to use the local emulator by exporting the PUBSUB_EMULATOR_HOST variable.
Question 262
Your ecommerce application receives external requests and forwards them to third-party API services for credit card processing, shipping, and inventory management as shown in the diagram.
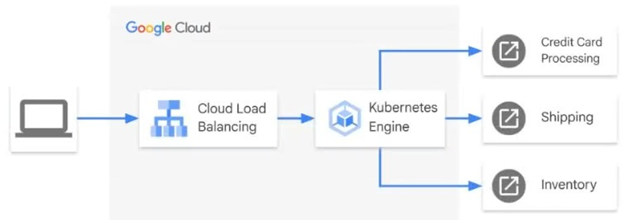
Your customers are reporting that your application is running slowly at unpredictable times. The application doesn’t report any metrics. You need to determine the cause of the inconsistent performance. What should you do?
A. Install the OpenTelemetry library for your respective language, and instrument your application.
B. Install the Ops Agent inside your container and configure it to gather application metrics.
C. Modify your application to read and forward the X-Cloud-Trace-Context header when it calls the downstream services.
D. Enable Managed Service for Prometheus on the Google Kubernetes Engine cluster to gather application metrics.
Question 263
You are developing a new application. You want the application to be triggered only when a given file is updated in your Cloud Storage bucket. Your trigger might change, so your process must support different types of triggers. You want the configuration to be simple so that multiple team members can update the triggers in the future. What should you do?
A. Configure Cloud Storage events to be sent to Pub/Sub, and use Pub/Sub events to trigger a Cloud Build job that executes your application.
B. Create an Eventarc trigger that monitors your Cloud Storage bucket for a specific filename, and set the target as Cloud Run.
C. Configure a Cloud Function that executes your application and is triggered when an object is updated in Cloud Storage.
D. Configure a Firebase function that executes your application and is triggered when an object is updated in Cloud Storage.
Question 264
You are defining your system tests for an application running in Cloud Run in a Google Cloud project. You need to create a testing environment that is isolated from the production environment. You want to fully automate the creation of the testing environment with the least amount of effort and execute automated tests. What should you do?
A. Using Cloud Build, execute Terraform scripts to create a new Google Cloud project and a Cloud Run instance of your application in the Google Cloud project.
B. Using Cloud Build, execute a Terraform script to deploy a new Cloud Run revision in the existing Google Cloud project. Use traffic splitting to send traffic to your test environment.
C. Using Cloud Build, execute gcloud commands to create a new Google Cloud project and a Cloud Run instance of your application in the Google Cloud project.
D. Using Cloud Build, execute gcloud commands to deploy a new Cloud Run revision in the existing Google Cloud project. Use traffic splitting to send traffic to your test environment.
Question 265
You are a cluster administrator for Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE). Your organization’s clusters are enrolled in a release channel. You need to be informed of relevant events that affect your GKE clusters, such as available upgrades and security bulletins. What should you do?
A. Configure cluster notifications to be sent to a Pub/Sub topic.
B. Execute a scheduled query against the google_cloud_release_notes BigQuery dataset.
C. Query the GKE API for available versions.
D. Create an RSS subscription to receive a daily summary of the GKE release notes.
Question 266
You are tasked with using C++ to build and deploy a microservice for an application hosted on Google Cloud. The code needs to be containerized and use several custom software libraries that your team has built. You do not want to maintain the underlying infrastructure of the application. How should you deploy the microservice?
A. Use Cloud Functions to deploy the microservice.
B. Use Cloud Build to create the container, and deploy it on Cloud Run.
C. Use Cloud Shell to containerize your microservice, and deploy it on a Container-Optimized OS Compute Engine instance.
D. Use Cloud Shell to containerize your microservice, and deploy it on standard Google Kubernetes Engine.
Question 267
You need to containerize a web application that will be hosted on Google Cloud behind a global load balancer with SSL certificates. You don’t have the time to develop authentication at the application level, and you want to offload SSL encryption and management from your application. You want to configure the architecture using managed services where possible. What should you do?
A. Host the application on Google Kubernetes Engine, and deploy an NGINX Ingress Controller to handle authentication.
B. Host the application on Google Kubernetes Engine, and deploy cert-manager to manage SSL certificates.
C. Host the application on Compute Engine, and configure Cloud Endpoints for your application.
D. Host the application on Google Kubernetes Engine, and use Identity-Aware Proxy (IAP) with Cloud Load Balancing and Google-managed certificates.
Question 268
You manage a system that runs on stateless Compute Engine VMs and Cloud Run instances. Cloud Run is connected to a VPC, and the ingress setting is set to Internal. You want to schedule tasks on Cloud Run. You create a service account and grant it the roles/run.invoker Identity and Access Management (IAM) role. When you create a schedule and test it, a 403 Permission Denied error is returned in Cloud Logging. What should you do?
A. Grant the service account the roles/run.developer IAM role.
B. Configure a cron job on the Compute Engine VMs to trigger Cloud Run on schedule.
C. Change the Cloud Run ingress setting to 'Internal and Cloud Load Balancing.'
D. Use Cloud Scheduler with Pub/Sub to invoke Cloud Run.
Question 269
You work on an application that relies on Cloud Spanner as its main datastore. New application features have occasionally caused performance regressions. You want to prevent performance issues by running an automated performance test with Cloud Build for each commit made. If multiple commits are made at the same time, the tests might run concurrently. What should you do?
A. Create a new project with a random name for every build. Load the required data. Delete the project after the test is run.
B. Create a new Cloud Spanner instance for every build. Load the required data. Delete the Cloud Spanner instance after the test is run.
C. Create a project with a Cloud Spanner instance and the required data. Adjust the Cloud Build build file to automatically restore the data to its previous state after the test is run.
D. Start the Cloud Spanner emulator locally. Load the required data. Shut down the emulator after the test is run.
Question 270
Your company's security team uses Identity and Access Management (IAM) to track which users have access to which resources. You need to create a version control system that can integrate with your security team's processes. You want your solution to support fast release cycles and frequent merges to your main branch to minimize merge conflicts. What should you do?
A. Create a Cloud Source Repositories repository, and use trunk-based development.
B. Create a Cloud Source Repositories repository, and use feature-based development.
C. Create a GitHub repository, mirror it to a Cloud Source Repositories repository, and use trunk-based development.
D. Create a GitHub repository, mirror it to a Cloud Source Repositories repository, and use feature-based development.
