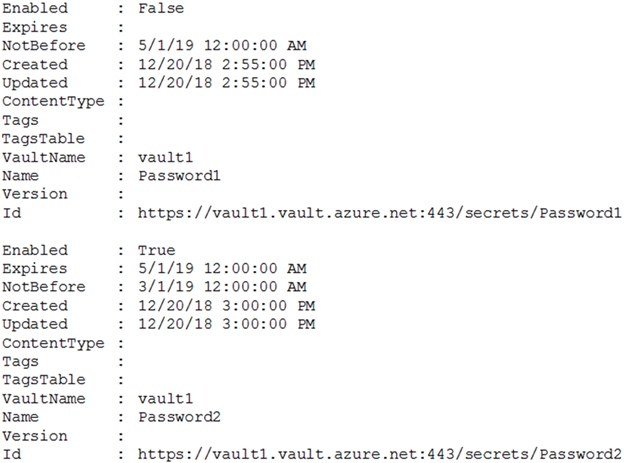
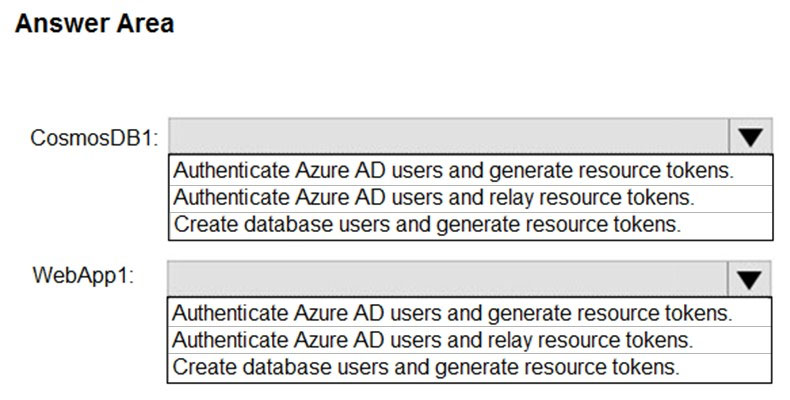
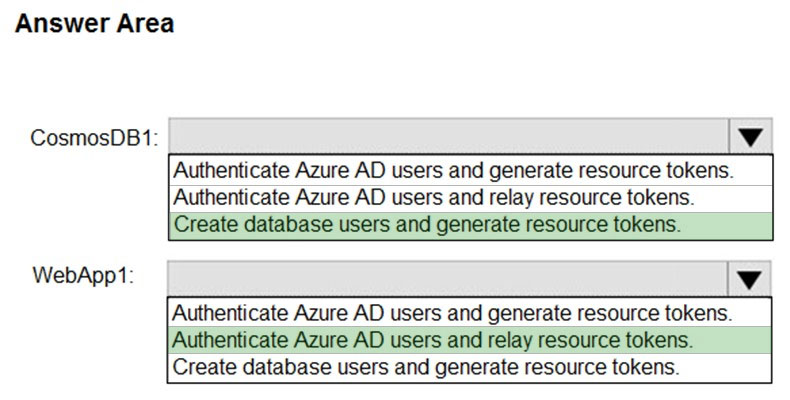
CosmosDB1: Create database users and generate resource tokens.
Azure Cosmos DB resource tokens provide a safe mechanism for allowing clients to read, write, and delete specific resources in an Azure Cosmos DB account according to the granted permissions.
WebApp1: Authenticate Azure AD users and relay resource tokens
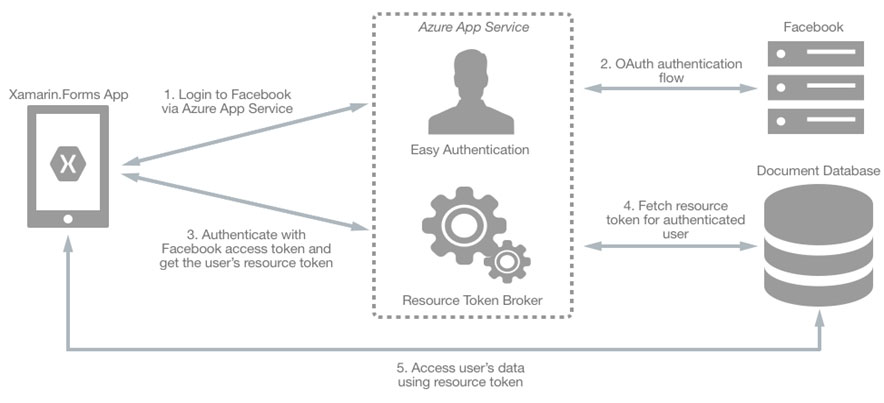
A typical approach to requesting, generating, and delivering resource tokens to a mobile application is to use a resource token broker. The following diagram shows a high-level overview of how the sample application uses a resource token broker to manage access to the document database data:
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/xamarin/xamarin-forms/data-cloud/cosmosdb/authentication