Question 181
You need to give new website users a globally unique identifier (GUID) using a service that takes in data points and returns a GUID. This data is sourced from both internal and external systems via HTTP calls that you will make via microservices within your pipeline. There will be tens of thousands of messages per second and that can be multi-threaded. and you worry about the backpressure on the system. How should you design your pipeline to minimize that backpressure?
A. Call out to the service via HTTP.
B. Create the pipeline statically in the class definition.
C. Create a new object in the startBundle method of DoFn.
D. Batch the job into ten-second increments.
Question 182
You are migrating your data warehouse to Google Cloud and decommissioning your on-premises data center. Because this is a priority for your company, you know that bandwidth will be made available for the initial data load to the cloud. The files being transferred are not large in number, but each file is 90 GB.
Additionally, you want your transactional systems to continually update the warehouse on Google Cloud in real time. What tools should you use to migrate the data and ensure that it continues to write to your warehouse?
A. Storage Transfer Service for the migration; Pub/Sub and Cloud Data Fusion for the real-time updates
B. BigQuery Data Transfer Service for the migration; Pub/Sub and Dataproc for the real-time updates
C. gsutil for the migration; Pub/Sub and Dataflow for the real-time updates
D. gsutil for both the migration and the real-time updates
Question 183
You are using Bigtable to persist and serve stock market data for each of the major indices. To serve the trading application, you need to access only the most recent stock prices that are streaming in. How should you design your row key and tables to ensure that you can access the data with the simplest query?
A. Create one unique table for all of the indices, and then use the index and timestamp as the row key design.
B. Create one unique table for all of the indices, and then use a reverse timestamp as the row key design.
C. For each index, have a separate table and use a timestamp as the row key design.
D. For each index, have a separate table and use a reverse timestamp as the row key design.
Question 184
You are building a report-only data warehouse where the data is streamed into BigQuery via the streaming API. Following Google's best practices, you have both a staging and a production table for the data. How should you design your data loading to ensure that there is only one master dataset without affecting performance on either the ingestion or reporting pieces?
A. Have a staging table that is an append-only model, and then update the production table every three hours with the changes written to staging.
B. Have a staging table that is an append-only model, and then update the production table every ninety minutes with the changes written to staging.
C. Have a staging table that moves the staged data over to the production table and deletes the contents of the staging table every three hours.
D. Have a staging table that moves the staged data over to the production table and deletes the contents of the staging table every thirty minutes.
Question 185
You issue a new batch job to Dataflow. The job starts successfully, processes a few elements, and then suddenly fails and shuts down. You navigate to the
Dataflow monitoring interface where you find errors related to a particular DoFn in your pipeline. What is the most likely cause of the errors?
A. Job validation
B. Exceptions in worker code
C. Graph or pipeline construction
D. Insufficient permissions
Question 186
Your new customer has requested daily reports that show their net consumption of Google Cloud compute resources and who used the resources. You need to quickly and efficiently generate these daily reports. What should you do?
A. Do daily exports of Cloud Logging data to BigQuery. Create views filtering by project, log type, resource, and user.
B. Filter data in Cloud Logging by project, resource, and user; then export the data in CSV format.
C. Filter data in Cloud Logging by project, log type, resource, and user, then import the data into BigQuery.
D. Export Cloud Logging data to Cloud Storage in CSV format. Cleanse the data using Dataprep, filtering by project, resource, and user.
Question 187
The Development and External teams have the project viewer Identity and Access Management (IAM) role in a folder named Visualization. You want the
Development Team to be able to read data from both Cloud Storage and BigQuery, but the External Team should only be able to read data from BigQuery. What should you do?
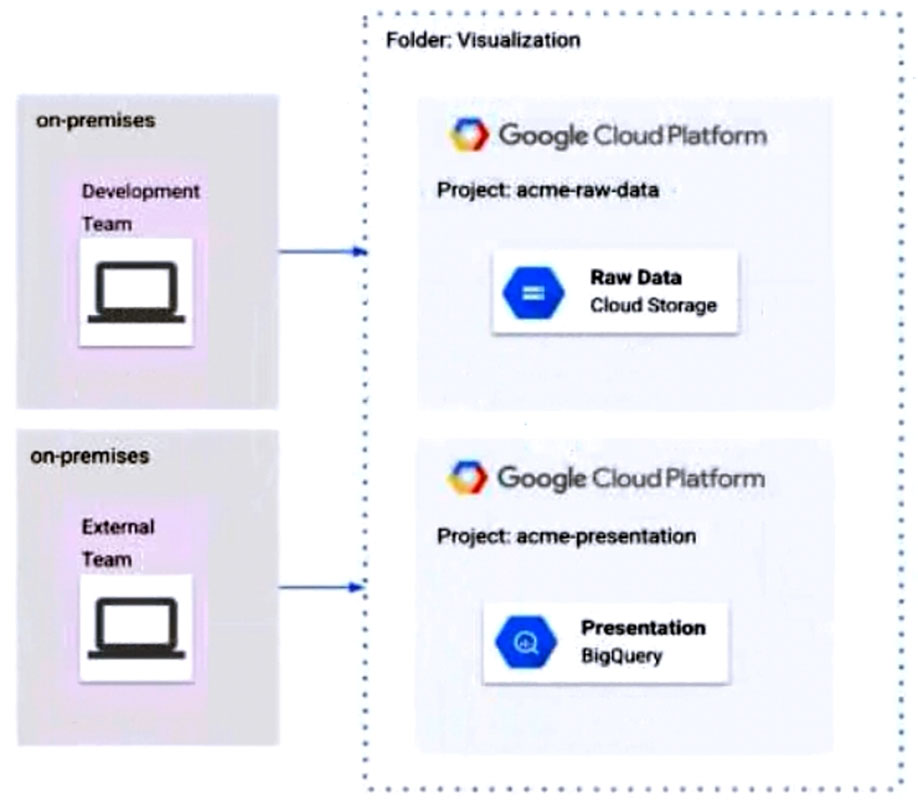
A. Remove Cloud Storage IAM permissions to the External Team on the acme-raw-data project.
B. Create Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) firewall rules on the acme-raw-data project that deny all ingress traffic from the External Team CIDR range.
C. Create a VPC Service Controls perimeter containing both projects and BigQuery as a restricted API. Add the External Team users to the perimeter's Access Level.
D. Create a VPC Service Controls perimeter containing both projects and Cloud Storage as a restricted API. Add the Development Team users to the perimeter's Access Level.
Question 188
Your startup has a web application that currently serves customers out of a single region in Asia. You are targeting funding that will allow your startup to serve customers globally. Your current goal is to optimize for cost, and your post-funding goal is to optimize for global presence and performance. You must use a native
JDBC driver. What should you do?
A. Use Cloud Spanner to configure a single region instance initially, and then configure multi-region Cloud Spanner instances after securing funding.
B. Use a Cloud SQL for PostgreSQL highly available instance first, and Bigtable with US, Europe, and Asia replication after securing funding.
C. Use a Cloud SQL for PostgreSQL zonal instance first, and Bigtable with US, Europe, and Asia after securing funding.
D. Use a Cloud SQL for PostgreSQL zonal instance first, and Cloud SQL for PostgreSQL with highly available configuration after securing funding.
Question 189
You need to migrate 1 PB of data from an on-premises data center to Google Cloud. Data transfer time during the migration should take only a few hours. You want to follow Google-recommended practices to facilitate the large data transfer over a secure connection. What should you do?
A. Establish a Cloud Interconnect connection between the on-premises data center and Google Cloud, and then use the Storage Transfer Service.
B. Use a Transfer Appliance and have engineers manually encrypt, decrypt, and verify the data.
C. Establish a Cloud VPN connection, start gcloud compute scp jobs in parallel, and run checksums to verify the data.
D. Reduce the data into 3 TB batches, transfer the data using gsutil, and run checksums to verify the data.
Question 190
You are loading CSV files from Cloud Storage to BigQuery. The files have known data quality issues, including mismatched data types, such as STRINGs and
INT64s in the same column, and inconsistent formatting of values such as phone numbers or addresses. You need to create the data pipeline to maintain data quality and perform the required cleansing and transformation. What should you do?
A. Use Data Fusion to transform the data before loading it into BigQuery.
B. Use Data Fusion to convert the CSV files to a self-describing data format, such as AVRO, before loading the data to BigQuery.
C. Load the CSV files into a staging table with the desired schema, perform the transformations with SQL, and then write the results to the final destination table.
D. Create a table with the desired schema, load the CSV files into the table, and perform the transformations in place using SQL.
