Question 151
You have provisioned a Dedicated Interconnect connection of 20 Gbps with a VLAN attachment of 10 Gbps. You recently noticed a steady increase in ingress traffic on the Interconnect connection from the on-premises data center. You need to ensure that your end users can achieve the full 20 Gbps throughput as quickly as possible. Which two methods can you use to accomplish this? (Choose two.)
A. Configure an additional VLAN attachment of 10 Gbps in another region. Configure the on-premises router to advertise routes with the same multi-exit discriminator (MED).
B. Configure an additional VLAN attachment of 10 Gbps in the same region. Configure the on-premises router to advertise routes with the same multi-exit discriminator (MED).
C. From the Google Cloud Console, modify the bandwidth of the VLAN attachment to 20 Gbps.
D. From the Google Cloud Console, request a new Dedicated Interconnect connection of 20 Gbps, and configure a VLAN attachment of 10 Gbps.
E. Configure Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) on the on-premises router to use the 20-Gbps Dedicated Interconnect connection.
Question 152
Your company has a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) with two Dedicated Interconnect connections in two different regions: us-west1 and us-east1. Each Dedicated Interconnect connection is attached to a Cloud Router in its respective region by a VLAN attachment. You need to configure a high availability failover path. By default, all ingress traffic from the on-premises environment should flow to the VPC using the us-west1 connection. If us-west1 is unavailable, you want traffic to be rerouted to us-east1. How should you configure the multi-exit discriminator (MED) values to enable this failover path?
A. Use regional routing. Set the us-east1 Cloud Router to a base priority of 100, and set the us-west1 Cloud Router to a base priority of 1
B. Use global routing. Set the us-east1 Cloud Router to a base priority of 100, and set the us-west1 Cloud Router to a base priority of 1
C. Use regional routing. Set the us-east1 Cloud Router to a base priority of 1000, and set the us-west1 Cloud Router to a base priority of 1
D. Use global routing. Set the us-east1 Cloud Router to a base priority of 1000, and set the us-west1 Cloud Router to a base priority of 1
Question 153
You have the following private Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) cluster deployment:
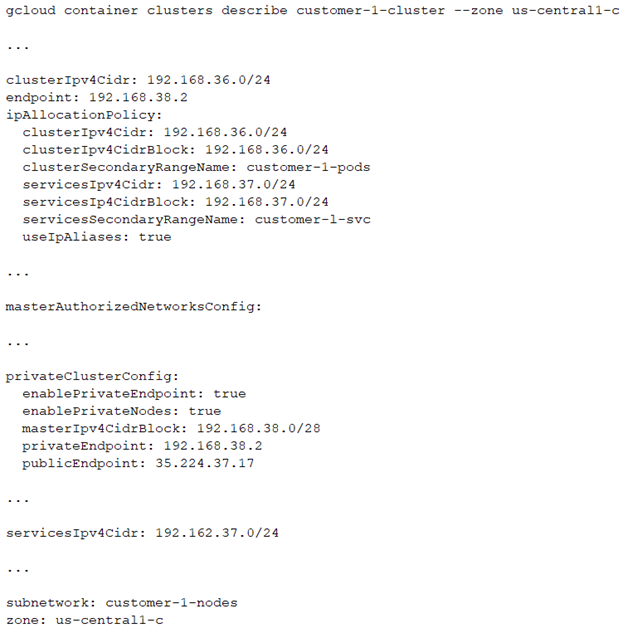
You have a virtual machine (VM) deployed in the same VPC in the subnetwork kubernetes-management with internal IP address 192.168.40 2/24 and no external IP address assigned. You need to communicate with the cluster master using kubectl. What should you do?
A. Add the network 192.168.40.0/24 to the masterAuthorizedNetworksConfig. Configure kubectl to communicate with the endpoint 192.168.38.2.
B. Add the network 192.168.38.0/28 to the masterAuthorizedNetworksConfig. Configure kubectl to communicate with the endpoint 192.168.38.2
C. Add the network 192.168.36.0/24 to the masterAuthorizedNetworksConfig. Configure kubectl to communicate with the endpoint 192.168.38.2
D. Add an external IP address to the VM, and add this IP address in the masterAuthorizedNetworksConfig. Configure kubectl to communicate with the endpoint 35.224.37.17.
Question 154
Your company's logo is published as an image file across multiple websites that are hosted by your company. You have implemented Cloud CDN; however, you want to improve the performance of the cache hit ratio associated with this image file. What should you do?
A. Configure custom cache keys for the backend service that holds the image file, and clear the Host and Protocol checkboxes.
B. Configure the default time to live (TTL) as 0 for the image file.
C. Configure versioned URLs for each domain to serve users the image file before the cache entry expires.
D. Configure Cloud Storage as a custom origin backend to host the image file, and select multi-region as the location type.
Question 155
Your company recently migrated to Google Cloud in a single region. You configured separate Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) networks for two departments: Department A and Department B. Department A has requested access to resources that are part of Department B's VPC. You need to configure the traffic from private IP addresses to flow between the VPCs using multi-NIC virtual machines (VMs) to meet security requirements. Your configuration also must:
• Support both TCP and UDP protocols
• Provide fully automated failover
• Include health-checks
• Require minimal manual intervention in the client VMs
Which approach should you take?
A. Create the VMs in the same zone, and configure static routes with IP addresses as next hops.
B. Create the VMs in different zones, and configure static routes with instance names as next hops.
C. Create an instance template and a managed instance group. Configure a single internal load balancer, and define a custom static route with the internal TCP/UDP load balancer as the next hop.
D. Create an instance template and a managed instance group. Configure two separate internal TCP/UDP load balancers for each protocol (TCP/UDP), and configure the client VMs to use the internal load balancers’ virtual IP addresses.
Question 156
You are designing an IP address scheme for new private Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) clusters. Due to IP address exhaustion of the RFC 1918 address space in your enterprise, you plan to use privately used public IP space for the new clusters. You want to follow Google-recommended practices. What should you do after designing your IP scheme?
A. Create the minimum usable RFC 1918 primary and secondary subnet IP ranges for the clusters. Re-use the secondary address range for the pods across multiple private GKE clusters.
B. Create the minimum usable RFC 1918 primary and secondary subnet IP ranges for the clusters, Re-use the secondary address range for the services across multiple private GKE clusters.
C. Create privately used public IP primary and secondary subnet ranges for the clusters. Create a private GKE cluster with the following options selected: --enable-ip-alias and --enable-private-nodes.
D. Create privately used public IP primary and secondary subnet ranges for the clusters. Create a private GKE cluster with the following options selected: --disable-default-snat, --enable-ip-alias, and --enable-private-nodes.
Question 157
You want Cloud CDN to serve the https://www.example.com/images/spacetime.png static image file that is hosted in a private Cloud Storage bucket. You are using the USE_ORIGIN_HEADERS cache mode. You receive an HTTP 403 error when opening the file in your browser, and you see that the HTTP response has a Cache-Control: private, max-age=0 header. How should you correct this issue?
A. Enable negative caching for the backend bucket.
B. Change the cache mode to Force cache all content.
C Configure a Cloud Storage bucket permission that gives allUsers the Storage Legacy Object Reader role.
D. Increase the default time-to-live (TTL) for the backend service.
Question 158
You are deploying an application that runs on Compute Engine instances. You need to determine how to expose your application to a new customer. You must ensure that your application meets the following requirements:
• Maps multiple existing reserved external IP addresses to the instance
• Processes IP Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP) traffic
What should you do?
A. Configure a target pool, and create protocol forwarding rules for each external IP address.
B. Configure a backend service, and create an external network load balancer for each external IP address.
C. Configure a target instance, and create a protocol forwarding rule for each external IP address to be mapped to the instance.
D. Configure the Compute Engine instances’ network interface external IP address from None to Ephemeral. Add as many external IP addresses as required.
Question 159
Your product team has web servers running on both us-east1 and us-west1 regions in the prod-servers project. Your security team plans to install an intrusion detection system (IDS) in their own Google Cloud project to inspect the incoming network traffic. What should you do?
A. Create a new project and a VPC for the security team.
Peer the new VPC with the web servers’ VPC in the prod-servers project.
Create an internal load balancer and the IDS system in both us-east1 and us-west1.
Enable Packet Mirroring, and create packet mirroring policies inside the new project.
C. Create a host project and a Sharad VPC for the security team.
Make prod-servers a service project, and relocate the web servers to shared subnets in both regions.
Enable IP forwarding on all the web servers.
Create the IDS system in a non-shared subnet of us-east1 or us-west1.
Configure the web servers to forward the packets to the IDS system.
C. Create a new project and a VPC for the security team.
Peer the new VPC with the web servers’ VPC in the prod-servers project.
Enable IP forwarding on all the web servers.
Install the IDS system in both us-east1 and us-west1.
Configure the web servers to forward the packets to the IDS system.
D. Create a host project and a Shared VPC for the security team.
Make prod-servers a service project, and relocate the web servers to shared subnets in both regions.
Create an internal load balancer and the IDS system in a subnet in either us-east1 or us-west1.
Enable Packet Mirroring, and create a packet mirroring policy inside the host project.
Question 160
You are in the process of deploying an internal HTTP(S) load balancer for your web server virtual machine (VM) instances. What two prerequisite tasks must be completed before creating the load balancer? (Choose two.)
A. Choose a region.
B. Create firewall rules for health checks.
C. Reserve a static IP address for the load balancer.
D. Determine the subnet mask for a proxy-only subnet.
E. Determine the subnet mask for Serverless VPC Access.
