Question 121
You want to share a Cloud Monitoring custom dashboard with a partner team. What should you do?
A. Provide the partner team with the dashboard URL to enable the partner team to create a copy of the dashboard.
B. Export the metrics to BigQuery. Use Looker Studio to create a dashboard, and share the dashboard with the partner team.
C. Copy the Monitoring Query Language (MQL) query from the dashboard, and send the ML query to the partner team.
D. Download the JSON definition of the dashboard, and send the JSON file to the partner team.
Question 122
You are building an application that runs on Cloud Run. The application needs to access a third-party API by using an API key. You need to determine a secure way to store and use the API key in your application by following Google-recommended practices. What should you do?
A. Save the API key in Secret Manager as a secret. Reference the secret as an environment variable in the Cloud Run application.
B. Save the API key in Secret Manager as a secret key. Mount the secret key under the /sys/api_key directory, and decrypt the key in the Cloud Run application.
C. Save the API key in Cloud Key Management Service (Cloud KMS) as a key. Reference the key as an environment variable in the Cloud Run application.
D. Encrypt the API key by using Cloud Key Management Service (Cloud KMS), and pass the key to Cloud Run as an environment variable. Decrypt and use the key in Cloud Run.
Question 123
You are currently planning how to display Cloud Monitoring metrics for your organization’s Google Cloud projects. Your organization has three folders and six projects:
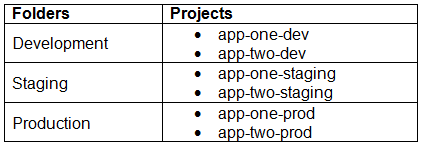
You want to configure Cloud Monitoring dashboards to only display metrics from the projects within one folder. You need to ensure that the dashboards do not display metrics from projects in the other folders. You want to follow Google-recommended practices. What should you do?
A. Create a single new scoping project.
B. Create new scoping projects for each folder.
C. Use the current app-one-prod project as the scoping project.
D. Use the current app-one-dev, app-one-staging, and app-one-prod projects as the scoping project for each folder.
Question 124
Your company’s security team needs to have read-only access to Data Access audit logs in the _Required bucket. You want to provide your security team with the necessary permissions following the principle of least privilege and Google-recommended practices. What should you do?
A. Assign the roles/logging.viewer role to each member of the security team.
B. Assign the roles/logging.viewer role to a group with all the security team members.
C. Assign the roles/logging.privateLogViewer role to each member of the security team.
D. Assign the roles/logging.privateLogViewer role to a group with all the security team members.
Question 125
Your team is building a service that performs compute-heavy processing on batches of data. The data is processed faster based on the speed and number of CPUs on the machine. These batches of data vary in size and may arrive at any time from multiple third-party sources. You need to ensure that third parties are able to upload their data securely. You want to minimize costs, while ensuring that the data is processed as quickly as possible. What should you do?
A. Provide a secure file transfer protocol (SFTP) server on a Compute Engine instance so that third parties can upload batches of data, and provide appropriate credentials to the server.
Create a Cloud Function with a google.storage.object.finalize Cloud Storage trigger. Write code so that the function can scale up a Compute Engine autoscaling managed instance group
Use an image pre-loaded with the data processing software that terminates the instances when processing completes.
B. Provide a Cloud Storage bucket so that third parties can upload batches of data, and provide appropriate Identity and Access Management (IAM) access to the bucket.
Use a standard Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) cluster and maintain two services: one that processes the batches of data, and one that monitors Cloud Storage for new batches of data.
Stop the processing service when there are no batches of data to process.
C. Provide a Cloud Storage bucket so that third parties can upload batches of data, and provide appropriate Identity and Access Management (IAM) access to the bucket.
Create a Cloud Function with a google.storage.object.finalize Cloud Storage trigger. Write code so that the function can scale up a Compute Engine autoscaling managed instance group.
Use an image pre-loaded with the data processing software that terminates the instances when processing completes.
D. Provide a Cloud Storage bucket so that third parties can upload batches of data, and provide appropriate Identity and Access Management (IAM) access to the bucket.
Use Cloud Monitoring to detect new batches of data in the bucket and trigger a Cloud Function that processes the data.
Set a Cloud Function to use the largest CPU possible to minimize the runtime of the processing.
Question 126
You are reviewing your deployment pipeline in Google Cloud Deploy. You must reduce toil in the pipeline, and you want to minimize the amount of time it takes to complete an end-to-end deployment. What should you do? (Choose two.)
A. Create a trigger to notify the required team to complete the next step when manual intervention is required.
B. Divide the automation steps into smaller tasks.
C. Use a script to automate the creation of the deployment pipeline in Google Cloud Deploy.
D. Add more engineers to finish the manual steps.
E. Automate promotion approvals from the development environment to the test environment.
Question 127
You work for a global organization and are running a monolithic application on Compute Engine. You need to select the machine type for the application to use that optimizes CPU utilization by using the fewest number of steps. You want to use historical system metrics to identify the machine type for the application to use. You want to follow Google-recommended practices. What should you do?
A. Use the Recommender API and apply the suggested recommendations.
B. Create an Agent Policy to automatically install Ops Agent in all VMs.
C. Install the Ops Agent in a fleet of VMs by using the gcloud CLI.
D. Review the Cloud Monitoring dashboard for the VM and choose the machine type with the lowest CPU utilization.
Question 128
You deployed an application into a large Standard Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) cluster. The application is stateless and multiple pods run at the same time. Your application receives inconsistent traffic. You need to ensure that the user experience remains consistent regardless of changes in traffic and that the resource usage of the cluster is optimized.
What should you do?
A. Configure a cron job to scale the deployment on a schedule
B. Configure a Horizontal Pod Autoscaler.
C. Configure a Vertical Pod Autoscaler
D. Configure cluster autoscaling on the node pool.
Question 129
You need to deploy a new service to production. The service needs to automatically scale using a managed instance group and should be deployed across multiple regions. The service needs a large number of resources for each instance and you need to plan for capacity. What should you do?
A. Monitor results of Cloud Trace to determine the optimal sizing.
B. Use the n2-highcpu-96 machine type in the configuration of the managed instance group.
C. Deploy the service in multiple regions and use an internal load balancer to route traffic.
D. Validate that the resource requirements are within the available project quota limits of each region.
Question 130
You are analyzing Java applications in production. All applications have Cloud Profiler and Cloud Trace installed and configured by default. You want to determine which applications need performance tuning. What should you do? (Choose two.)
A. Examine the wall-clock time and the CPU time of the application. If the difference is substantial increase the CPU resource allocation.
B. Examine the wall-clock time and the CPU time of the application. If the difference is substantial, increase the memory resource allocation.
C. Examine the wall-clock time and the CPU time of the application. If the difference is substantial, increase the local disk storage allocation.
D. Examine the latency time the wall-clock time and the CPU time of the application. If the latency time is slowly burning down the error budget, and the difference between wall-clock time and CPU time is minimal mark the application for optimization.
E. Examine the heap usage of the application. If the usage is low, mark the application for optimization.
