Question 91
You work for a global organization and run a service with an availability target of 99% with limited engineering resources.
For the current calendar month, you noticed that the service has 99.5% availability. You must ensure that your service meets the defined availability goals and can react to business changes, including the upcoming launch of new features.
You also need to reduce technical debt while minimizing operational costs. You want to follow Google-recommended practices. What should you do?
A. Add N+1 redundancy to your service by adding additional compute resources to the service.
B. Identify, measure, and eliminate toil by automating repetitive tasks.
C. Define an error budget for your service level availability and minimize the remaining error budget.
D. Allocate available engineers to the feature backlog while you ensure that the service remains within the availability target.
Question 92
You are developing the deployment and testing strategies for your CI/CD pipeline in Google Cloud. You must be able to:
• Reduce the complexity of release deployments and minimize the duration of deployment rollbacks.
• Test real production traffic with a gradual increase in the number of affected users.
You want to select a deployment and testing strategy that meets your requirements. What should you do?
A. Recreate deployment and canary testing
B. Blue/green deployment and canary testing
C. Rolling update deployment and A/B testing
D. Rolling update deployment and shadow testing
Question 93
You are creating a CI/CD pipeline to perform Terraform deployments of Google Cloud resources. Your CI/CD tooling is running in Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) and uses an ephemeral Pod for each pipeline run. You must ensure that the pipelines that run in the Pods have the appropriate Identity and Access Management (IAM) permissions to perform the Terraform deployments. You want to follow Google-recommended practices for identity management. What should you do? (Choose two.)
A. Create a new Kubernetes service account, and assign the service account to the Pods. Use Workload Identity to authenticate as the Google service account.
B. Create a new JSON service account key for the Google service account, store the key as a Kubernetes secret, inject the key into the Pods, and set the GOOGLE_APPLICATION_CREDENTIALS environment variable.
C. Create a new Google service account, and assign the appropriate IAM permissions.
D. Create a new JSON service account key for the Google service account, store the key in the secret management store for the CI/CD tool, and configure Terraform to use this key for authentication.
E. Assign the appropriate IAM permissions to the Google service account associated with the Compute Engine VM instances that run the Pods.
Question 94
You are the on-call Site Reliability Engineer for a microservice that is deployed to a Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) Autopilot cluster. Your company runs an online store that publishes order messages to Pub/Sub, and a microservice receives these messages and updates stock information in the warehousing system. A sales event caused an increase in orders, and the stock information is not being updated quickly enough. This is causing a large number of orders to be accepted for products that are out of stock. You check the metrics for the microservice and compare them to typical levels:
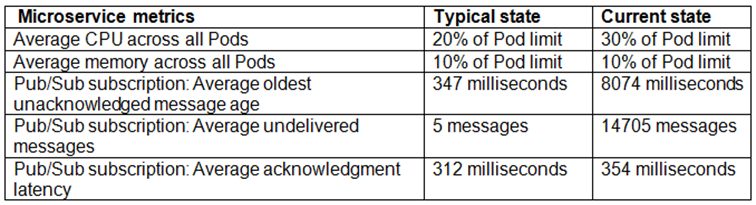
You need to ensure that the warehouse system accurately reflects product inventory at the time orders are placed and minimize the impact on customers. What should you do?
A. Decrease the acknowledgment deadline on the subscription.
B. Add a virtual queue to the online store that allows typical traffic levels.
C. Increase the number of Pod replicas.
D. Increase the Pod CPU and memory limits.
Question 95
Your team deploys applications to three Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) environments: development, staging, and production. You use GitHub repositories as your source of truth. You need to ensure that the three environments are consistent. You want to follow Google-recommended practices to enforce and install network policies and a logging DaemonSet on all the GKE clusters in those environments. What should you do?
A. Use Google Cloud Deploy to deploy the network policies and the DaemonSet. Use Cloud Monitoring to trigger an alert if the network policies and DaemonSet drift from your source in the repository.
B. Use Google Cloud Deploy to deploy the DaemonSet and use Policy Controller to configure the network policies. Use Cloud Monitoring to detect drifts from the source in the repository and Cloud Functions to correct the drifts.
C. Use Cloud Build to render and deploy the network policies and the DaemonSet. Set up Config Sync to sync the configurations for the three environments.
D. Use Cloud Build to render and deploy the network policies and the DaemonSet. Set up a Policy Controller to enforce the configurations for the three environments.
Question 96
You are using Terraform to manage infrastructure as code within a CI/CD pipeline. You notice that multiple copies of the entire infrastructure stack exist in your Google Cloud project, and a new copy is created each time a change to the existing infrastructure is made. You need to optimize your cloud spend by ensuring that only a single instance of your infrastructure stack exists at a time. You want to follow Google-recommended practices. What should you do?
A. Create a new pipeline to delete old infrastructure stacks when they are no longer needed.
B. Confirm that the pipeline is storing and retrieving the terraform.tfstate file from Cloud Storage with the Terraform gcs backend.
C. Verify that the pipeline is storing and retrieving the terraform.tfstate file from a source control.
D. Update the pipeline to remove any existing infrastructure before you apply the latest configuration.
Question 97
You are creating Cloud Logging sinks to export log entries from Cloud Logging to BigQuery for future analysis. Your organization has a Google Cloud folder named Dev that contains development projects and a folder named Prod that contains production projects. Log entries for development projects must be exported to dev_dataset, and log entries for production projects must be exported to prod_dataset. You need to minimize the number of log sinks created, and you want to ensure that the log sinks apply to future projects. What should you do?
A. Create a single aggregated log sink at the organization level.
B. Create a log sink in each project.
C. Create two aggregated log sinks at the organization level, and filter by project ID.
D. Create an aggregated log sink in the Dev and Prod folders.
Question 98
Your company runs services by using multiple globally distributed Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) clusters. Your operations team has set up workload monitoring that uses Prometheus-based tooling for metrics, alerts, and generating dashboards. This setup does not provide a method to view metrics globally across all clusters. You need to implement a scalable solution to support global Prometheus querying and minimize management overhead. What should you do?
A. Configure Prometheus cross-service federation for centralized data access.
B. Configure workload metrics within Cloud Operations for GKE.
C. Configure Prometheus hierarchical federation for centralized data access.
D. Configure Google Cloud Managed Service for Prometheus.
Question 99
You need to build a CI/CD pipeline for a containerized application in Google Cloud. Your development team uses a central Git repository for trunk-based development. You want to run all your tests in the pipeline for any new versions of the application to improve the quality. What should you do?
A. 1. Install a Git hook to require developers to run unit tests before pushing the code to a central repository.
2. Trigger Cloud Build to build the application container. Deploy the application container to a testing environment, and run integration tests.
3. If the integration tests are successful, deploy the application container to your production environment, and run acceptance tests.
B. 1. Install a Git hook to require developers to run unit tests before pushing the code to a central repository. If all tests are successful, build a container.
2. Trigger Cloud Build to deploy the application container to a testing environment, and run integration tests and acceptance tests.
3. If all tests are successful, tag the code as production ready. Trigger Cloud Build to build and deploy the application container to the production environment.
C. 1. Trigger Cloud Build to build the application container, and run unit tests with the container.
2. If unit tests are successful, deploy the application container to a testing environment, and run integration tests.
3. If the integration tests are successful, the pipeline deploys the application container to the production environment. After that, run acceptance tests.
D. 1. Trigger Cloud Build to run unit tests when the code is pushed. If all unit tests are successful, build and push the application container to a central registry.
2. Trigger Cloud Build to deploy the container to a testing environment, and run integration tests and acceptance tests.
3. If all tests are successful, the pipeline deploys the application to the production environment and runs smoke tests
Question 100
The new version of your containerized application has been tested and is ready to be deployed to production on Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE). You could not fully load-test the new version in your pre-production environment, and you need to ensure that the application does not have performance problems after deployment. Your deployment must be automated. What should you do?
A. Deploy the application through a continuous delivery pipeline by using canary deployments. Use Cloud Monitoring to look for performance issues, and ramp up traffic as supported by the metrics.
B. Deploy the application through a continuous delivery pipeline by using blue/green deployments. Migrate traffic to the new version of the application and use Cloud Monitoring to look for performance issues.
C. Deploy the application by using kubectl and use Config Connector to slowly ramp up traffic between versions. Use Cloud Monitoring to look for performance issues.
D. Deploy the application by using kubectl and set the spec.updateStrategy.type field to RollingUpdate. Use Cloud Monitoring to look for performance issues, and run the kubectl rollback command if there are any issues.
