Question 321
Your team plans to use AlloyDB as their database backend for an upcoming application release. Your application is currently hosted in a different project and network than the AlloyDB instances. You need to securely connect your application to the AlloyDB instance while keeping the projects isolated. You want to minimize additional operations and follow Google-recommended practices. How should you configure the network for database connectivity?
A. Provision a Shared VPC project where both the application project and the AlloyDB project are service projects.
B. Use AlloyDB Auth Proxy and configure the application project’s firewall to allow connections to port 5433.
C. Provision a service account from the AlloyDB project. Use this service account’s JSON key file as the --credentials-file to connect to the AlloyDB instance.
D. Ask the database team to provision AlloyDB databases in the same project and network as the application.
Question 322
You have an on-premises containerized service written in the current stable version of Python 3 that is available only to users in the United States. The service has high traffic during the day and no traffic at night. You need to migrate this application to Google Cloud and track error logs after the migration in Error Reporting. You want to minimize the cost and effort of these tasks. What should you do?
A. Deploy the code on Cloud Run. Configure your code to write errors to standard error.
B. Deploy the code on Cloud Run. Configure your code to stream errors to a Cloud Storage bucket.
C. Deploy the code on a GKE Autopilot cluster. Configure your code to write error logs to standard error.
D. Deploy the code on a GKE Autopilot cluster. Configure your code to write error logs to a Cloud Storage bucket.
Question 323
Your team is developing a new application that is packaged as a container and stored in Artifact Registry. You are responsible for configuring the CI/CD pipelines that use Cloud Build. Containers may be pushed manually as a local development effort or in an emergency. Every time a new container is pushed to Artifact Registry, you need to trigger another Cloud Build pipeline that executes a vulnerability scan. You want to implement this requirement using the least amount of effort. What should you do?
A. Configure Artifact Registry to publish a message to a Pub/Sub topic when a new image is pushed. Configure the vulnerability scan pipeline to be triggered by the Pub/Sub message.
B. Configure the Cloud Build Cl pipeline that publishes the new image to send a message to a Pub/Sub topic that triggers the vulnerability scan pipeline.
C. Configure Artifact Registry to publish a message to a Pub/Sub topic when a new image is pushed. Configure Pub/Sub to invoke a Cloud Function that triggers the vulnerability scan pipeline.
D. Use Cloud Scheduler to periodically check for new versions of the container in Artifact Registry and trigger the vulnerability scan pipeline.
Question 324
You have an application running on a GKE cluster. Your application has a stateless web frontend, and has a high-availability requirement. Your cluster is set to automatically upgrade, and some of your nodes need to be drained. You need to ensure that the application has a serving capacity of 10% of the Pods prior to the drain. What should you do?
A. Configure a Vertical Pod Autoscaler (VPA) to increase the memory and CPU by 10% and set the updateMode to Auto.
B. Configure the Pod replica count to be 10% more than the current replica count.
C. Configure a Pod Disruption Budget (PDB) value to have a minAvailable value of 10%.
D. Configure the Horizontal Pod Autoscaler (HPA) maxReplicas value to 10% more than the current replica count.
Question 325
You are designing an application that shares PDF files containing time-sensitive information with users. The PDF files are saved in Cloud Storage. You need to provide secure access to the files.
You have the following requirements:
• Users should only have access to files that they are allowed to view.
• Users should be able to request to read, write, or delete the PDF files for 24 hours.
Not all users of the application have a Google account. How should you provide access to data objects?
A. Configure the application to generate signed URLs with an expiration time of 24 hours. Share the signed URLs with users. Attach the signed URL to the PDF files that users require access to.
B. Provide users with the Service Account Token Creator IAM role to impersonate the application's service account. Assign the Cloud Storage User IAM role to the application's service account to access the Cloud Storage bucket. Rotate the application's service account key every 24 hours.
C. Generate a service account that grants access to the POF files. Configure the application to provide users with a download link to the service account's key file. Set an expiration time of 24 hours to the service account Keys. Instruct users to authenticate by using the service account key file.
D. Assign the Storage Object User IAM role to users that request access to the PDF files. Set an IAM condition on the role to expire after 24 hours.
Question 326
You have developed a Python application that you want to containerize and deploy to Cloud Run. You have developed a Cloud Build pipeline with the following steps:
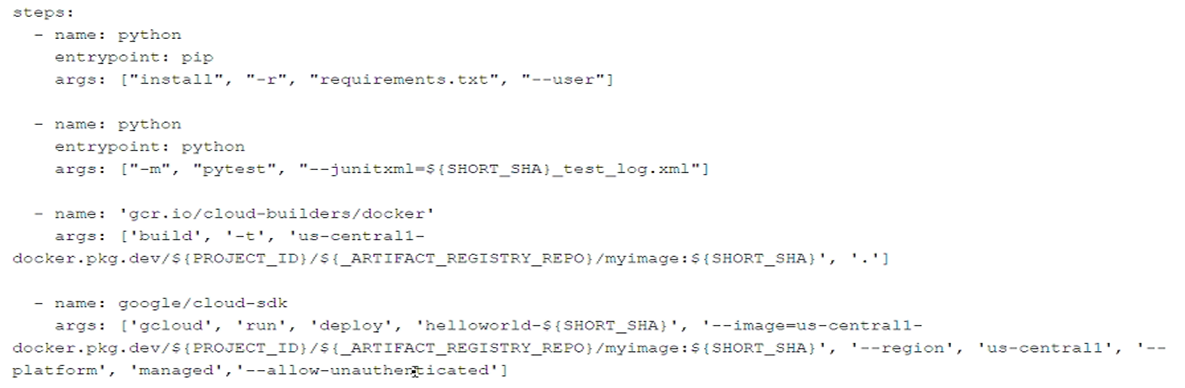
After triggering the pipeline, you notice in the Cloud Build logs that the final step of the pipeline fails and the container is unable to be deployed to Cloud Run. What is the cause of this issue, and how should you resolve it?
A. The final step uses a Cloud Run instance name that does not match the container name. Update the deployment step so that the Cloud Run instance name matches the container name, and rerun the pipeline.
B. The Docker container image has not been pushed to Artifact Registry. Add a step to the pipeline to push the application container image to Artifact Registry, and rerun the pipeline.
C. Cloud Run does not allow unauthenticated invocations. Remove the --allow-unauthenticated parameter to enforce authentication on the application, and rerun the pipeline.
D. Unit tests in the pipeline are failing. Update the application code so that all unit tests pass, and rerun the pipeline.
Question 327
Your infrastructure team uses Terraform Cloud and manages Google Cloud resources by using Terraform configuration files. You want to configure an infrastructure as code pipeline that authenticates to Google Cloud APIs. You want to use the most secure approach and minimize changes to the configuration. How should you configure the authentication?
A. Use Terraform on GKE. Create a Kubernetes service account to execute the Terraform code. Use workload identity federation to authenticate as the Google service account.
B. Install Terraform on a Compute Engine VM. Configure the VM by using a service account that has the required permissions to manage the Google Cloud resources.
C. Configure Terraform Cloud to use workload identity federation to authenticate to the Google Cloud APIs.
D. Create a service account that has the required permissions to manage the Google Cloud resources, and import the service account key to Terraform Cloud. Use this service account to authenticate to the Google Cloud APIs.
Question 328
Your team has created an application that is hosted on a GKE cluster. You need to connect the application to a REST service that is deployed in two GKE clusters in two different regions. How should you set up the connection and health checks? (Choose two.)
A. Use Cloud Service Mesh with sidecar proxies to connect the application to the REST service.
B. Use Cloud Service Mesh with proxyless gRPC to connect the application to the REST service.
C. Configure the REST service's firewall to allow health checks originating from the GKE service’s IP ranges.
D. Configure the REST service's firewall to allow health checks originating from the GKE control plane’s IP ranges.
E. Configure the REST service's firewall to allow health checks originating from the GKE check probe’s IP ranges.
Question 329
You are using the latest stable version of Python 3 to develop an API that stores data in a Cloud SQL database. You need to perform CRUD operations on the production database securely and reliably with minimal effort. What should you do?
A. 1. Use Cloud Composer to manage the connection to the Cloud SQL database from your Python application.
2. Grant an IAM role to the service account that includes the composer.worker permission.
B. 1. Use the Cloud SQL API to connect to the Cloud SQL database from your Python application.
2. Grant an IAM role to the service account that includes the cloudsql.instances.login permission.
C. 1. Use the Cloud SQL connector library for Python to connect to the Cloud SQL database through a Cloud SQL Auth Proxy.
2. Grant an IAM role to the service account that includes the cloudsql.instances.connect permission.
D. 1. Use the Cloud SQL emulator to connect to the Cloud SQL database from Cloud Shell
2. Grant an IAM role to the user that includes the cloudsql.instances.login permission.
Question 330
Your company manages an application that captures stock data in an internal database. You need to create an API that provides real-time stock data to users. You want to return stock data to users as quickly as possible, and you want your solution to be highly scalable. What should you do?
A. Create a BigQuery dataset and table to act as the internal database. Query the table when user requests are received.
B. Create a Memorystore for Redis instance to store all stock market data. Query this database when user requests are received.
C. Create a Bigtable instance. Query the table when user requests are received. Configure a Pub/Sub topic to queue user requests that your API will respond to.
D. Create a Memorystore for Redis instance, and use this database to store the most accessed stock data. Query this instance first when user requests are received, and fall back to the internal database.
