Question 61
Which three criteria can a FortiGate use to look for a matching firewall policy to process traffic? (Choose three.)
A. Highest to lowest priority defined in the firewall policy.
B. Services defined in the firewall policy.
C. Source defined as Internet Services in the firewall policy.
D. Lowest to highest policy ID number.
E. Destination defined as Internet Services in the firewall policy.
Question 62
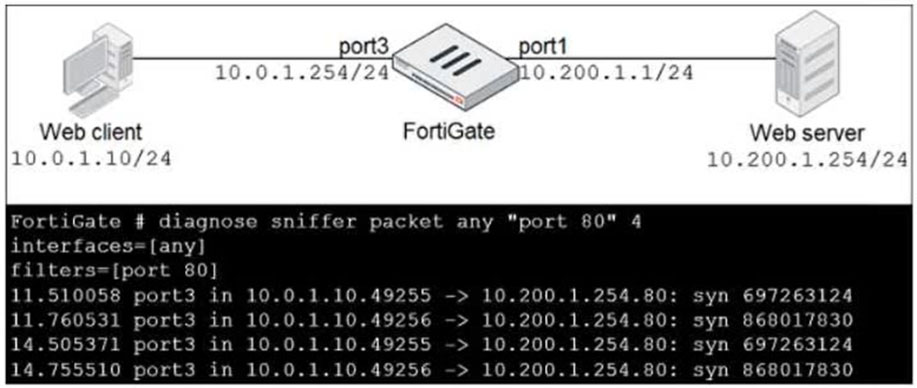
Refer to the exhibit.
In the network shown in the exhibit, the web client cannot connect to the HTTP web server. The administrator runs the FortiGate built-in sniffer and gets the output as shown in the exhibit.
What should the administrator do next to troubleshoot the problem?
A. Execute a debug flow.
B. Run a sniffer on the web server.
C. Capture the traffic using an external sniffer connected to port1.
D. Execute another sniffer in the FortiGate, this time with the filter "host 10.0.1.10".
Question 63
Which three CLI commands can you use to troubleshoot Layer 3 issues if the issue is in neither the physical layer nor the link layer? (Choose three.)
A. execute ping
B. diagnose sys top
C. get system arp
D. execute traceroute
E. diagnose sniffer packet any
Question 64
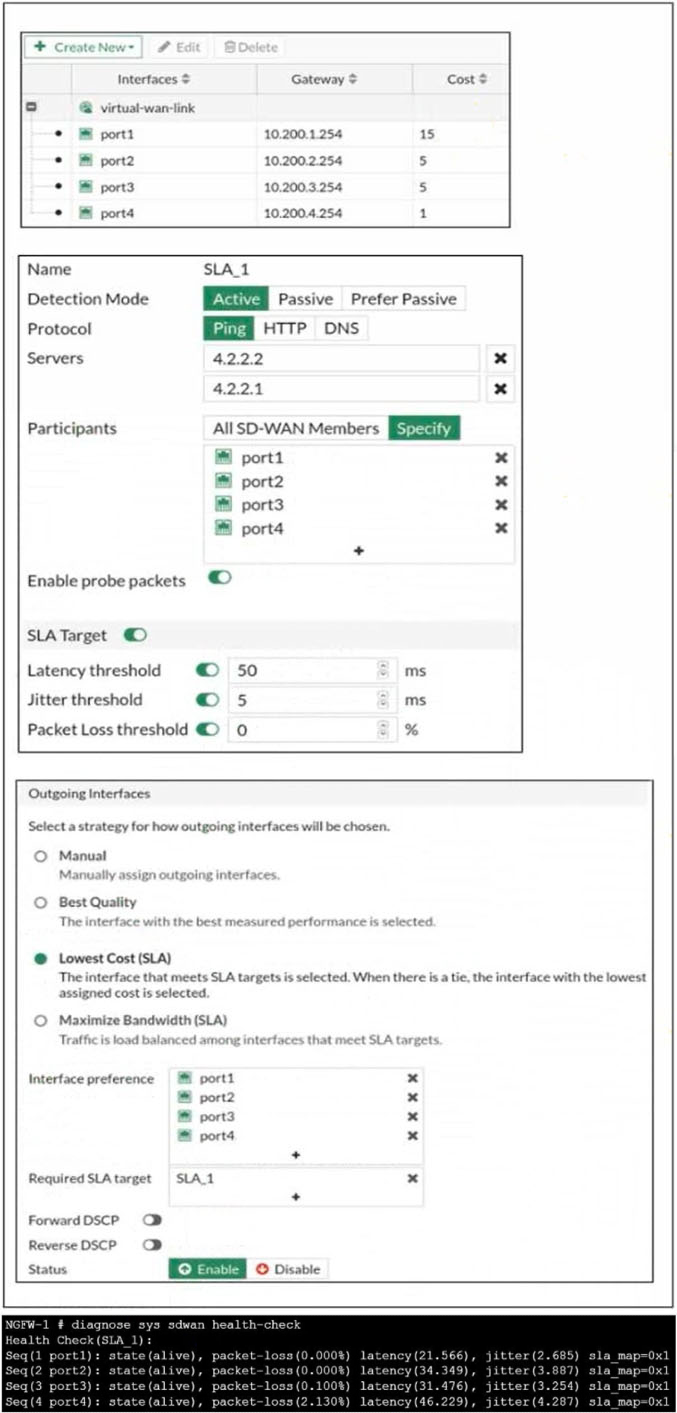
Refer to the exhibits.
The exhibit shows the configuration for the SD-WAN member, Performance SLA, and SD-WAN Rule, as well as the output of diagnose sys virtual-wan- link health-check.
Which interface will be selected as an outgoing interface?
A. port2
B. port3
C. port4
D. port1
Question 65
Which two statements are true about the RPF check? (Choose two.)
A. The RPF check is run on the first sent packet of any new session.
B. The RPF check is run on the first reply packet of any new session.
C. The RPF check is run on the first sent and reply packet of any new session.
D. RPF is a mechanism that protects FortiGate and your network from IP spoofing attacks.
Question 66
Which three pieces of information does FortiGate use to identify the hostname of the SSL server when SSL certificate inspection is enabled? (Choose three.)
A. The subject field in the server certificate
B. The subject alternative name (SAN) field in the server certificate
C. The serial number in the server certificate
D. The server name indication (SNI) extension in the client hello message
E. The host field in the HTTP header
Question 67
FortiGate is operating in NAT mode and is configured with two virtual LAN (VLAN) subinterfaces added to the same physical interface.
In this scenario, which statement about the VLAN IDs is true?
A. The two VLAN subinterfaces can have the same VLAN ID only if they have IP addresses in the same subnet.
B. The two VLAN subinterfaces can have the same VLAN ID only if they have IP addresses in different subnets.
C. The two VLAN subinterfaces can have the same VLAN ID only if they belong to different VDOMs.
D. The two VLAN subinterfaces must have different VLAN IDs.
Question 68
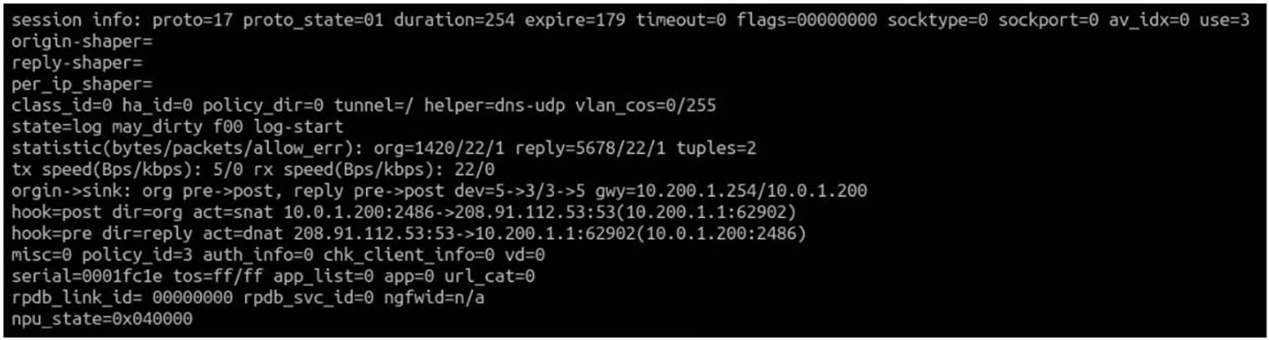
Refer to the exhibit, which contains a session diagnostic output.
Which statement is true about the session diagnostic output?
A. The session is in TCP ESTABLISHED state.
B. The session is a bidirectional UDP connection.
C. The session is a UDP unidirectional state.
D. The session is a bidirectional TCP connection.
Question 69
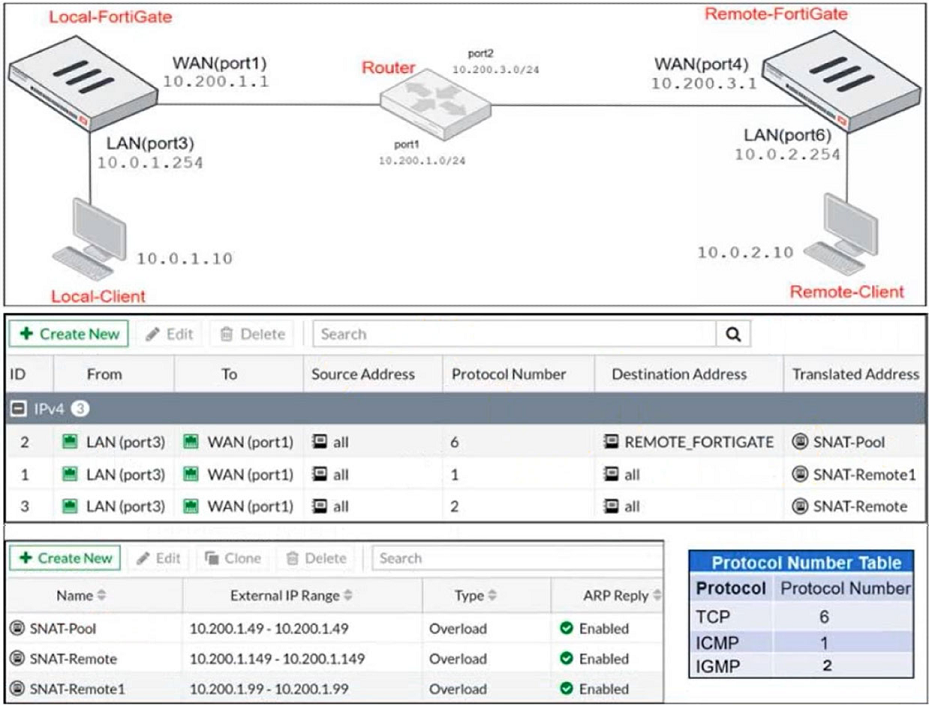
Refer to the exhibits.
The exhibits contain a network diagram, central SNAT policy, and IP pool configuration.
The WAN (port1) interface has the IP address 10.200.1.1/24.
The LAN (port3) interface has the IP address 10.0.1.254/24.
A firewall policy is configured to allow all destinations from LAN (port3) to WAN (port1).
Central NAT is enabled, so NAT settings from matching Central SNAT policies will be applied.
Which IP address will be used to source NAT the traffic, if the user on Local-Client (10.0.1.10) pings the IP address of Remote-FortiGate (10.200.3.1)?
A. 10.200.1.99
B. 10.200.1.149
C. 10.200.1.1
D. 10.200.1.49
Question 70
Which scanning technique on FortiGate can be enabled only on the CLI?
A. Antivirus scan
B. Machine learning scan
C. Trojan scan
D. Ransomware scan



