Question 131
An architect must address sustained congestion on the access and distribution uplinks of a network. QoS has already been implemented and optimized, but it is no longer effective in ensuring optimal network performance. Which two solutions should the architect use to improve network performance. (Choose two.)
A. Configure selective packet discard to drop noncritical network traffic.
B. Bundle additional uplinks into logical EtherChannels.
C. Utilize random early detection to manage queues.
D. Implement higher-speed uplink interfaces.
E. Reconfigure QoS based on the IntServ model.
Question 132
An engineer must design a QoS solution for a customer that is connected to an ISP over a 1Gbps link with a 100Mbps CIR. The ISP aggressively drops all traffic received over the CIR, which is causing numerous TCP retransmissions. The customer is not using any RTP applications but wants to maximize bandwidth usage up to the CIR. Which QoS solution should the engineer choose?
A. policing
B. queuing
C. traffic shaping
D. policer with markdown
Question 133
The customer solution requires QoS to support streaming multimedia over a WAN. An architect chooses to use Per-Hop Behavior. Which solution should the engineer use to classify and mark traffic traveling between branch sites?
A. CBWFQ with DSCP AF2
B. LLQ with DSCP EF
C. CBWFQ with DSCP AF3
D. LLQ with DSCP AF4
Question 134
An engineer must design an in-band management solution for a customer with branch sites. The solution must allow remote management of the branch sites using management protocols over an MPLS WAN. Queueing is implemented at the remote sites using these classes:
- Class1 equals voice traffic
- Class2 equals mission-critical traffic
- Class3 equals default trafficHow must the solution prioritize the management traffic over the WAN?
A. Mark the traffic with DSCP EF and map into Class1 with a minimum bandwidth assigned by reducing the bandwidth available to Class2.
B. Mark the traffic with DSCP CS1 and map into Class2 with a minimum bandwidth assigned by reducing the bandwidth available to Class3.
C. Mark the traffic with DSCP CS6 and map into Class1 with a minimum bandwidth assigned by reducing the bandwidth available to Class2.
D. Mark the traffic with DSCP CS2 and map into Class2 with a minimum bandwidth assigned by reducing the bandwidth available to Class3.
Question 135
An engineer is designing a multicast network for a company specializing in VoD content. Receivers are across the Internet, and for performance reasons, the multicast framework must be close to the receivers within each AS. For high availability, if the sources in one AS are no longer available, the receivers of that AS must be able to receive the VoD content from the sources in another AS. Which feature must the design include?
A. SSM
B. anycast RP
C. bidirectional PIM
D. MSDP
Question 136
Which type of rendezvous point deployment is standards-based and supports dynamic RP discovery?
A. bootstrap router
B. Anycast-RP
C. Auto-RP
D. static RP
Question 137
An engineer must design a QoS solution for a customer. The network currently supports data only, but the customer will roll out VoIP and IP video in conjunction with the new QoS solution. The engineer plans to use DiffServ. To ensure priority for voice services, which model must the design include?
A. 8-class model
B. 4-class model
C. 6-class model
D. 12-class model
Question 138
Which NETCONF operation creates filtering that is specific to the session notifications?
A. <create-subscription>
B. <commit>
C. <notification>
D. <logging>
Question 139
DRAG DROP -Drag and drop the characteristics from the left onto the telemetry mode they apply to on the right.
Select and Place:
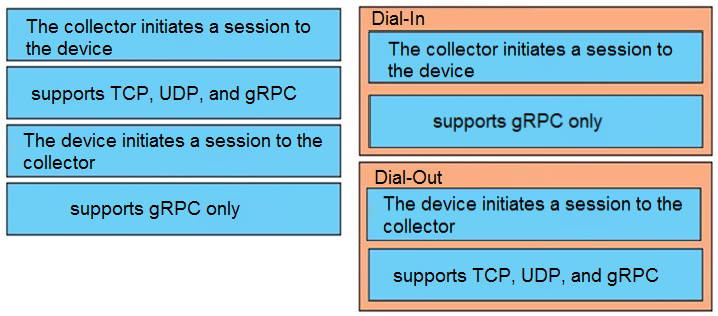
Question 140
An engineer needs a standards-driven YANG model to manage a multivendor network environment. Which model should the engineer choose?
A. Native
B. OpenConfig
C. IETF
D. IEEE NETCONF

