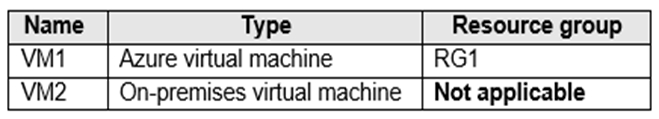
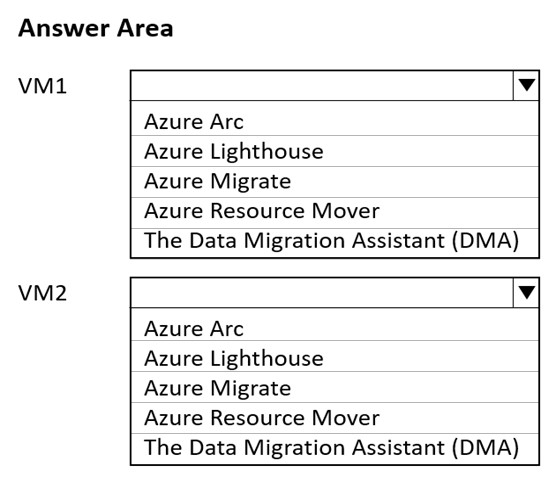
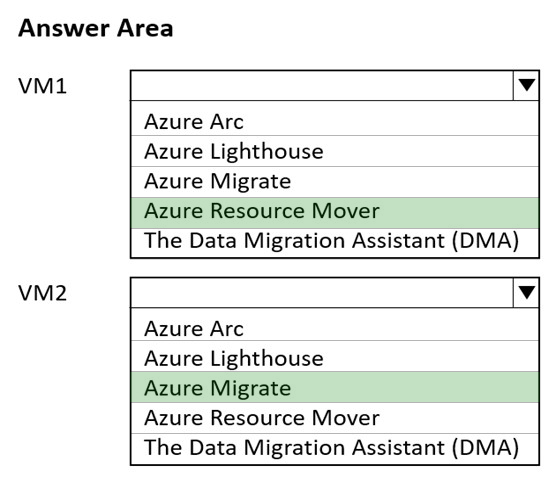
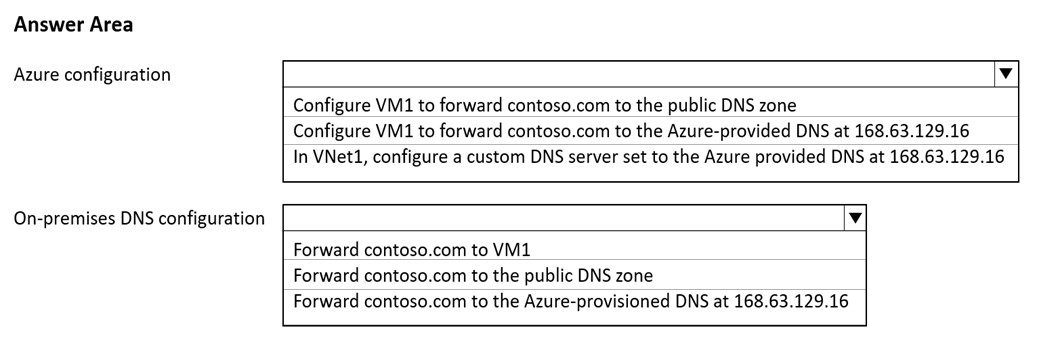
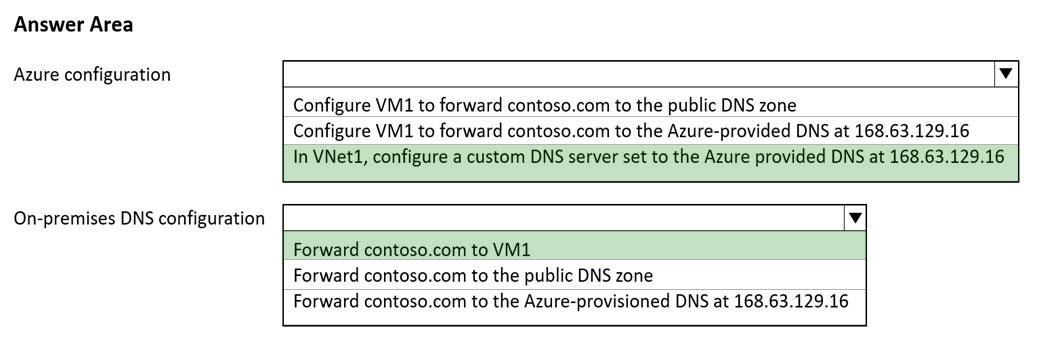
Box 1:In VNET1, configure a custom DNS server set to the Azure provided DNS at 168.63.129.16
Virtual network workloads without custom DNS server.
This configuration is appropriate for virtual network workloads without a custom DNS server. In this scenario, the client queries for the private endpoint IP address to the Azure-provided DNS service 168.63.129.16. Azure DNS will be responsible for DNS resolution of the private DNS zones.
The following screenshot illustrates the DNS resolution sequence from virtual network workloads using the private DNS zone:
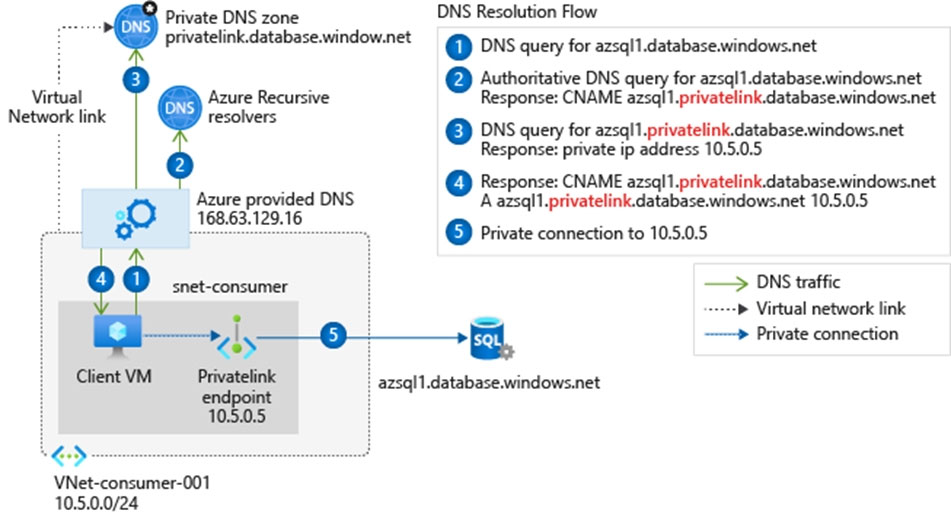
Box 2: Forward contoso.com to VM1
Forward to the DNS server VM1.
Note: You can use the following options to configure your DNS settings for private endpoints:
* Use the host file (only recommended for testing). You can use the host file on a virtual machine to override the DNS.
* Use a private DNS zone. You can use private DNS zones to override the DNS resolution for a private endpoint. A private DNS zone can be linked to your virtual network to resolve specific domains.
* Use your DNS forwarder (optional). You can use your DNS forwarder to override the DNS resolution for a private link resource. Create a DNS forwarding rule to use a private DNS zone on your DNS server hosted in a virtual network.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/private-link/private-endpoint-dns