Question 241
You are designing the architecture of your application to store data in Cloud Storage. Your application consists of pipelines that read data from a Cloud Storage bucket that contains raw data, and write the data to a second bucket after processing. You want to design an architecture with Cloud Storage resources that are capable of being resilient if a Google Cloud regional failure occurs. You want to minimize the recovery point objective (RPO) if a failure occurs, with no impact on applications that use the stored data. What should you do?
A. Adopt multi-regional Cloud Storage buckets in your architecture.
B. Adopt two regional Cloud Storage buckets, and update your application to write the output on both buckets.
C. Adopt a dual-region Cloud Storage bucket, and enable turbo replication in your architecture.
D. Adopt two regional Cloud Storage buckets, and create a daily task to copy from one bucket to the other.
Question 242
You have designed an Apache Beam processing pipeline that reads from a Pub/Sub topic. The topic has a message retention duration of one day, and writes to a Cloud Storage bucket. You need to select a bucket location and processing strategy to prevent data loss in case of a regional outage with an RPO of 15 minutes. What should you do?
A. 1. Use a dual-region Cloud Storage bucket.
2. Monitor Dataflow metrics with Cloud Monitoring to determine when an outage occurs.
3. Seek the subscription back in time by 15 minutes to recover the acknowledged messages.
4. Start the Dataflow job in a secondary region.
B. 1. Use a multi-regional Cloud Storage bucket.
2. Monitor Dataflow metrics with Cloud Monitoring to determine when an outage occurs.
3. Seek the subscription back in time by 60 minutes to recover the acknowledged messages.
4. Start the Dataflow job in a secondary region.
C. 1. Use a regional Cloud Storage bucket.
2. Monitor Dataflow metrics with Cloud Monitoring to determine when an outage occurs.
3. Seek the subscription back in time by one day to recover the acknowledged messages.
4. Start the Dataflow job in a secondary region and write in a bucket in the same region.
D. 1. Use a dual-region Cloud Storage bucket with turbo replication enabled.
2. Monitor Dataflow metrics with Cloud Monitoring to determine when an outage occurs.
3. Seek the subscription back in time by 60 minutes to recover the acknowledged messages.
4. Start the Dataflow job in a secondary region.
Question 243
You are preparing data that your machine learning team will use to train a model using BigQueryML. They want to predict the price per square foot of real estate. The training data has a column for the price and a column for the number of square feet. Another feature column called ‘feature1’ contains null values due to missing data. You want to replace the nulls with zeros to keep more data points. Which query should you use?
A.

B.

C.

D.

Question 244
Different teams in your organization store customer and performance data in BigQuery. Each team needs to keep full control of their collected data, be able to query data within their projects, and be able to exchange their data with other teams. You need to implement an organization-wide solution, while minimizing operational tasks and costs. What should you do?
A. Ask each team to create authorized views of their data. Grant the biquery.jobUser role to each team.
B. Create a BigQuery scheduled query to replicate all customer data into team projects.
C. Ask each team to publish their data in Analytics Hub. Direct the other teams to subscribe to them.
D. Enable each team to create materialized views of the data they need to access in their projects.
Question 245
You are developing a model to identify the factors that lead to sales conversions for your customers. You have completed processing your data. You want to continue through the model development lifecycle. What should you do next?
A. Use your model to run predictions on fresh customer input data.
B. Monitor your model performance, and make any adjustments needed.
C. Delineate what data will be used for testing and what will be used for training the model.
D. Test and evaluate your model on your curated data to determine how well the model performs.
Question 246
You have one BigQuery dataset which includes customers’ street addresses. You want to retrieve all occurrences of street addresses from the dataset. What should you do?
A. Write a SQL query in BigQuery by using REGEXP_CONTAINS on all tables in your dataset to find rows where the word “street” appears.
B. Create a deep inspection job on each table in your dataset with Cloud Data Loss Prevention and create an inspection template that includes the STREET_ADDRESS infoType.
C. Create a discovery scan configuration on your organization with Cloud Data Loss Prevention and create an inspection template that includes the STREET_ADDRESS infoType.
D. Create a de-identification job in Cloud Data Loss Prevention and use the masking transformation.
Question 247
Your company operates in three domains: airlines, hotels, and ride-hailing services. Each domain has two teams: analytics and data science, which create data assets in BigQuery with the help of a central data platform team. However, as each domain is evolving rapidly, the central data platform team is becoming a bottleneck. This is causing delays in deriving insights from data, and resulting in stale data when pipelines are not kept up to date. You need to design a data mesh architecture by using Dataplex to eliminate the bottleneck. What should you do?
A. 1. Create one lake for each team. Inside each lake, create one zone for each domain.
2. Attach each of the BigQuery datasets created by the individual teams as assets to the respective zone.
3. Have the central data platform team manage all zones’ data assets.
B. 1. Create one lake for each team. Inside each lake, create one zone for each domain.
2. Attach each of the BigQuery datasets created by the individual teams as assets to the respective zone.
3. Direct each domain to manage their own zone’s data assets.
C. 1. Create one lake for each domain. Inside each lake, create one zone for each team.
2. Attach each of the BigQuery datasets created by the individual teams as assets to the respective zone.
3. Direct each domain to manage their own lake’s data assets.
D. 1. Create one lake for each domain. Inside each lake, create one zone for each team.
2. Attach each of the BigQuery datasets created by the individual teams as assets to the respective zone.
3. Have the central data platform team manage all lakes’ data assets.
Question 248
dataset.inventory_vm sample records:
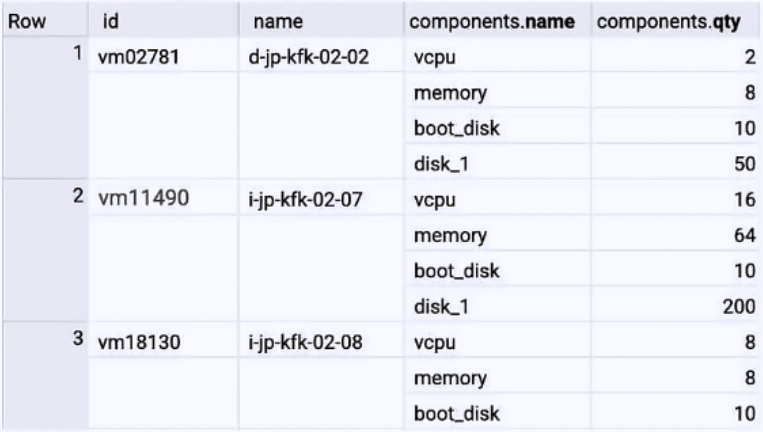
You have an inventory of VM data stored in the BigQuery table. You want to prepare the data for regular reporting in the most cost-effective way. You need to exclude VM rows with fewer than 8 vCPU in your report. What should you do?
A. Create a view with a filter to drop rows with fewer than 8 vCPU, and use the UNNEST operator.
B. Create a materialized view with a filter to drop rows with fewer than 8 vCPU, and use the WITH common table expression.
C. Create a view with a filter to drop rows with fewer than 8 vCPU, and use the WITH common table expression.
D. Use Dataflow to batch process and write the result to another BigQuery table.
Question 249
Your team is building a data lake platform on Google Cloud. As a part of the data foundation design, you are planning to store all the raw data in Cloud Storage. You are expecting to ingest approximately 25 GB of data a day and your billing department is worried about the increasing cost of storing old data. The current business requirements are:
• The old data can be deleted anytime.
• There is no predefined access pattern of the old data.
• The old data should be available instantly when accessed.
• There should not be any charges for data retrieval.
What should you do to optimize for cost?
A. Create the bucket with the Autoclass storage class feature.
B. Create an Object Lifecycle Management policy to modify the storage class for data older than 30 days to nearline, 90 days to coldline, and 365 days to archive storage class. Delete old data as needed.
C. Create an Object Lifecycle Management policy to modify the storage class for data older than 30 days to coldline, 90 days to nearline, and 365 days to archive storage class. Delete old data as needed.
D. Create an Object Lifecycle Management policy to modify the storage class for data older than 30 days to nearline, 45 days to coldline, and 60 days to archive storage class. Delete old data as needed.
Question 250
Your company's data platform ingests CSV file dumps of booking and user profile data from upstream sources into Cloud Storage. The data analyst team wants to join these datasets on the email field available in both the datasets to perform analysis. However, personally identifiable information (PII) should not be accessible to the analysts. You need to de-identify the email field in both the datasets before loading them into BigQuery for analysts. What should you do?
A. 1. Create a pipeline to de-identify the email field by using recordTransformations in Cloud Data Loss Prevention (Cloud DLP) with masking as the de-identification transformations type.
2. Load the booking and user profile data into a BigQuery table.
B. 1. Create a pipeline to de-identify the email field by using recordTransformations in Cloud DLP with format-preserving encryption with FFX as the de-identification transformation type.
2. Load the booking and user profile data into a BigQuery table.
C. 1. Load the CSV files from Cloud Storage into a BigQuery table, and enable dynamic data masking.
2. Create a policy tag with the email mask as the data masking rule.
3. Assign the policy to the email field in both tables. A
4. Assign the Identity and Access Management bigquerydatapolicy.maskedReader role for the BigQuery tables to the analysts.
D. 1. Load the CSV files from Cloud Storage into a BigQuery table, and enable dynamic data masking.
2. Create a policy tag with the default masking value as the data masking rule.
3. Assign the policy to the email field in both tables.
4. Assign the Identity and Access Management bigquerydatapolicy.maskedReader role for the BigQuery tables to the analysts




